期刊论文 查看更多论文列表
ECC-NeRF: Anti-Aliasing Neural Radiance Fields with Elliptic Cone-Casting for Diverse Camera Models
Haidong Qin, Tao Yang, Xiaoshi Zhou, Dongdong Li, Yanran Dai, Jing Li.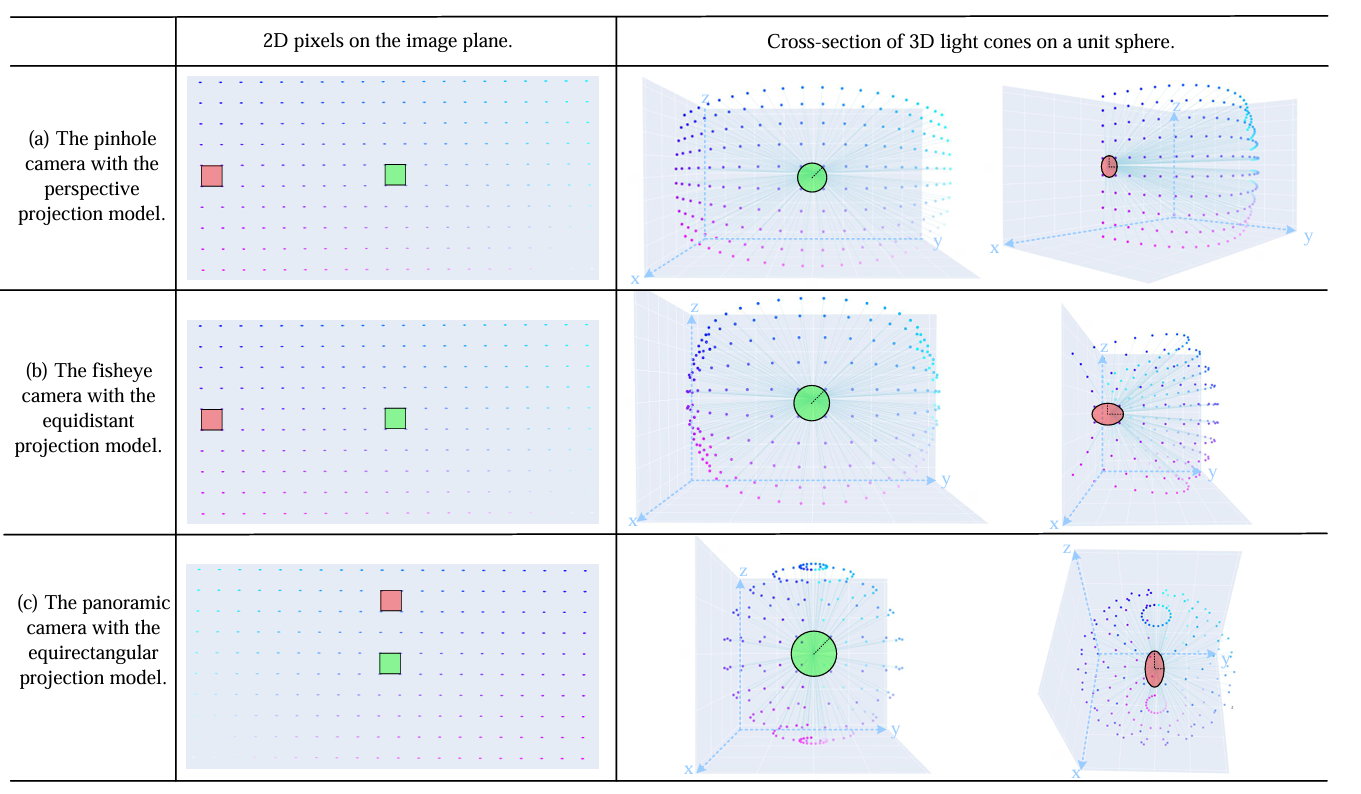
Anti-aliasing is a crucial research topic in computer graphics, which can significantly enhance the rendering quality of neural radiance fields (NeRF). Recent studies have introduced effective anti-aliasing NeRF methods, utilizing cone-casting to replace ray-casting and modeling the 3D observation area of pixels as circular cones. The cone-casting strategy has successfully reduced blurring and aliasing in novel view rendering. However, we have observed that the light cones are not standard circular cones because the camera projection model distorts them into elliptic cones of diverse sizes and shapes. This finding motivates us to model pixel light cones as anisotropic elliptic cones and propose an elliptic cone-casting-based anti-aliasing NeRF method called “ECC-NeRF". Specifically, we first derive the elliptic cone models for common pinhole, fisheye, and panoramic cameras based on their camera projection models. Then, we integrate the proposed elliptic cone-casting into two representative cone-casting-based anti-aliasing NeRF methods: Mip-NeRF and Zip-NeRF. Our experimental evaluations on multiple datasets demonstrate that our method can achieve more accurate multi-scale anisotropic representation and better novel view rendering quality with negligible additional computation cost.
Read MoreRT3DHVC: A Real-time Human Holographic Video Conferencing System with a Consumer RGB-D Camera Array
Yuqi Jiang, Jing Li, Yanran Dai, Haidong Qin, Xiaoshi Zhou, Yong Zhang, Hongwei Liu , Kefan Yan, and Tao Yang.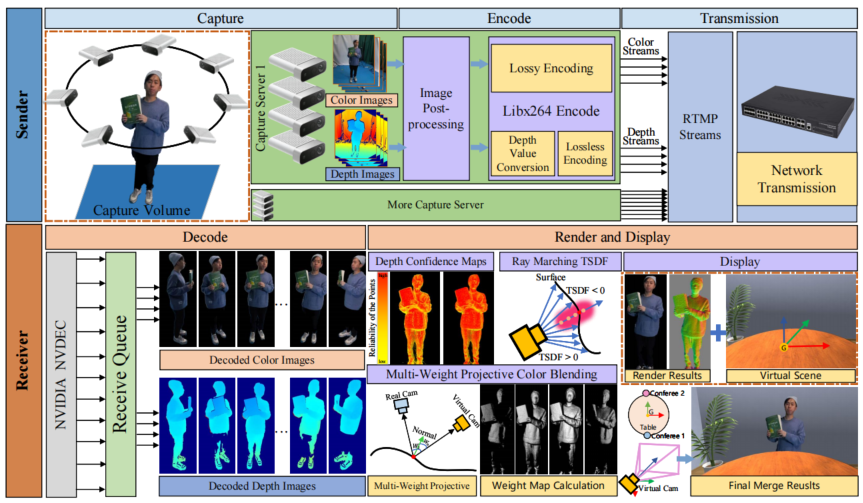
In this paper, we present an end-to-end holographic video conferencing system that enables real-time high-quality free-viewpoint rendering of participants in different spatial regions, placing them in a unified virtual space for a more immersive display. Our system offers a cost-effective, complete holographic conferencing process, including multiview 3D data capture, RGB-D stream compression and transmission, high-quality rendering, and immersive display. It employs a sparse set of commodity RGB-D cameras that capture 3D geometric and textural information. We then remotely transmit color and depth maps via standard video encoding and transmission protocols. We propose a GPU-parallelized rendering pipeline based on an image-based virtual view synthesis algorithm to achieve real-time and high-quality scene rendering. This algorithm uses an on-the-fly Truncated Signed Distance Function (TSDF) approach, which marches along virtual rays within a computed precise search interval to determine surface intersections. We then design a multiweight projective texture mapping method to fuse color information from multiple views. Furthermore, we introduce a method that uses a depth confidence map to weight the rendering results from different views, which mitigates the impact of sensor noise and inaccurate measurements on the rendering results. Finally, our system places conference participants from different spaces into a virtual conference environment with a global coordinate system through coordinate transformation, which simulates a real conference scene in physical space, providing an immersive remote conferencing experience. Experimental evaluations confirm our system’s real-time, low-latency, high-quality, and immersive capabilities.
Read MoreDepth-Enhanced Panoramic Image Stitching for Real-Time Longwall Face Monitoring
Jiayang Nie, Jing Li, Guodong Zhang, Yuqi Jiang, Canbin Zhang, Jianxing Song, Jing Liu, and Tao Yang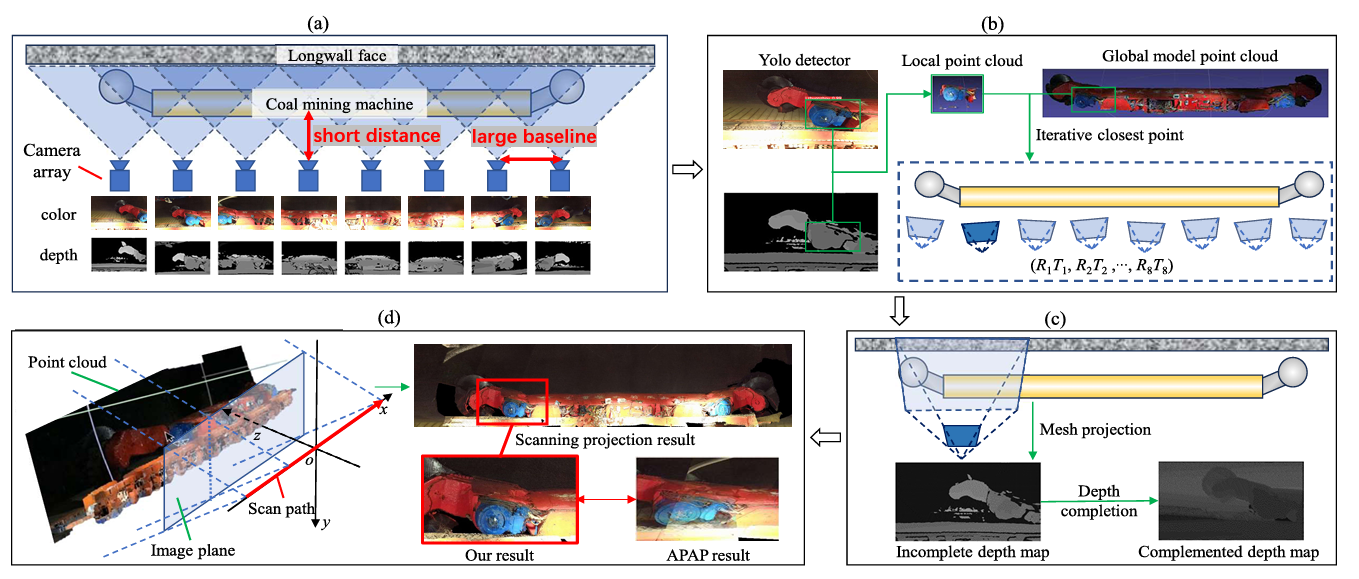
We presents a novel panoramic stitching solution for real-time monitoring of longwall mining faces, addressing significant parallax issues inherent in underground environments. Using a depth camera array and leveraging a local point cloud registration method, our method enhances real-time monitoring, ensuring precise scene alignment measurement and object placement in dynamic environments. Furthermore, we introduce depth completion to resolve issues related to incomplete depth data and propose a scan projection method to maintain image integrity in constrained, tunnel-like spaces. Our system has been validated in both real and simulated environments. The experimental results demonstrate superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods, with an operational speed of 25 fps.
Read MoreGS-SFS: Joint Gaussian Splatting and Shape-from-Silhouette for Multiple Human Reconstruction in Large-Scale Sports Scenes
Yuqi Jiang, Jing Li, Haidong Qin, Yanran Dai, Jing Liu, Guodong Zhang, Canbin Zhang, and Tao Yang.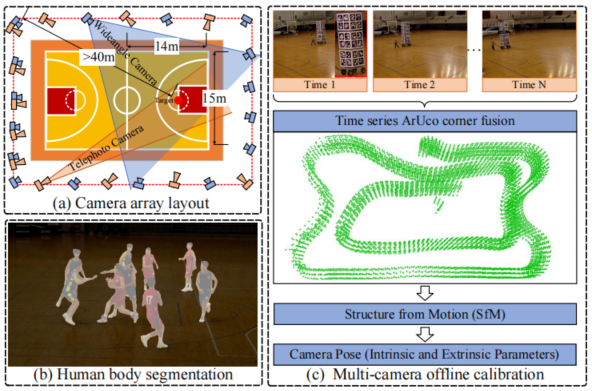
We introduce GS-SFS, a method that utilizes a camera array with wide baselines for high-quality multiple human mesh reconstruction in large-scale sports scenes. Traditional human reconstruction methods in sports scenes, such as Shape-from-Silhouette (SFS), struggle with sparse camera setups and small human targets, making it challenging to obtain complete and accurate human representations. Despite advances in differentiable rendering, including 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), which can produce photorealistic novel-view renderings with dense inputs, accurate depiction of surfaces and generation of detailed meshes is still challenging. Our approach uniquely combines 3DGS’s view synthesis with an optimized SFS method, thereby significantly enhancing the quality of multiperson mesh reconstruction in large-scale sports scenes. Specifically, we introduce body shape priors, including the human surface point clouds extracted through SFS and human silhouettes, to constrain 3DGS to a more accurate representation of the human body only. Then, we develop an improved mesh reconstruction method based on SFS, mainly by adding additional viewpoints through 3DGS and obtaining a more accurate surface to achieve higher-quality reconstruction models. We implement a high-density scene resampling strategy based on spherical sampling of human bounding boxes and render new perspectives using 3D Gaussian Splatting to create precise and dense multi-view human silhouettes. During mesh reconstruction, we integrate the human body’s 2D Signed Distance Function (SDF) into the computation of the SFS’s implicit surface field, resulting in smoother and more accurate surfaces. Moreover, we enhance mesh texture mapping by blending original and rendered images with different weights, preserving high-quality textures while compensating for missing details. The experimental results from real basketball game scenarios demonstrate the significant improvements of our approach for multiple human body model reconstruction in complex sports settings.
Read MoreInside-Out Multiperson 3-D Pose Estimation Using the Panoramic Camera Capture System
Haidong Qin, Yanran Dai, Yuqi Jiang, Dongdong Li, Hongwei Liu, Yong Zhang, Jing Li, Tao Yang.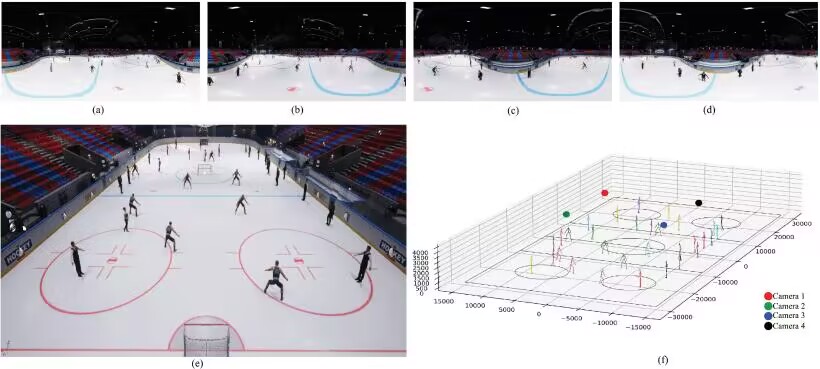
Estimating the 3-D human poses of multiple individuals using multiple cameras is a significant research topic within the field of vision-based measurement. Contrary to the classical outside-in camera capture system, the inside-out panoramic camera capture system can cover larger scenes with fewer cameras for 3-D human pose estimation. This advancement extends the application of 3-D human pose measurement beyond small spaces like motion capture studios. For example, this approach can be utilized for intelligent security surveillance in broad outdoor squares or capturing athletes’ movements in large-scale sports scenes. However, existing inside-out 3-D human pose estimation methods that utilize panoramic cameras encounter challenges, particularly in multiperson occlusion scenarios. Aimed at these problems, this article presents a novel inside-out multiperson 3-D human pose estimation method using just a few calibrated panoramic cameras. Specifically, we first propose a cross-view multiperson matching algorithm based on panoramic camera epipolar geometry constraint to improve human body matching robustness across viewpoints. Then, we take advantage of multiple panoramic cameras and introduce a multiview human pose clustering and fusion algorithm to improve the average recall (AR) of 3-D human pose estimation. In addition, we propose a multiview human pose nonlinear optimization algorithm to jointly optimize the weighted reprojection errors of estimated 3-D human poses, which can further improve the average precision (AP). We have conducted extensive experiments on the public Panoptic Studio dataset and self-built real and simulated datasets to demonstrate that our method can inside-out estimate 3-D human poses using multiple panoramic cameras. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, the 3-D human pose omission is greatly reduced through the complementarity of multiple cameras, and the precision of 3-D human pose estimation is largely improved by utilizing multicamera observation information.
Read MoreScene-Constrained Neural Radiance Fields for High-Quality Sports Scene Rendering Based on Visual Sensor Network
Yanran Dai, Jing Li, Yong Zhang, Yuqi Jiang, Haidong Qin, Xiaoshi Zhou, Yidan Zhang, Tao Yang.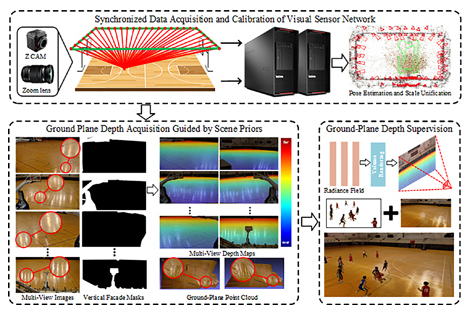
Free-viewpoint videos offer audiences a more immersive and liberated way to watch sports. The rendering of sports scenes encompasses two essential elements: dynamic targets and static scenes. While much current research focuses on achieving high-quality rendering of human bodies, rendering large-scale sports scenes presents various challenges. Sports arenas are characterized by large spatial extents, restricted camera placement, uncontrollable lighting, weak textures, and repetitive patterns, all of which pose significant obstacles to achieving high-quality scene rendering. In this work, we propose a neural radiance field rendering method based on scene-prior geometric constraints. We introduce prior 3-D geometric dimensions and 2-D semantic masks, to derive high-precision ground plane depth maps from camera imaging parameters. This is a geometry-based method that does not rely on visual features, and thus, it is unaffected by insufficient textures, repetition, and reflections. Subsequently, we apply ground depth maps as geometric consistency constraints to optimize the neural rendering network, thereby reducing the impact of color inconsistencies across viewpoints. The visual sensor network we build can synchronously capture static fields and dynamic targets in sports scenes. Based on the visual sensor network, we collected multiviewpoint datasets of large-scale sports scenes at Invengo and Xidian Gymnasium for performance evaluation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can generate high-precision and cross-viewpoint scale-consistent depth constraints and helps reduce holes and artifacts in synthesized views. Our method outperforms the state of the art (SOTA) for novel view rendering for challenging large-scale sports scenes.
Read MoreReal-time Distance Field Acceleration based Free Viewpoint Video Synthesis in Large Sport Field
Yanran Dai, Jing Li, Yuqi Jiang, Haidong Qin, Bang Liang, Shikuan Hong, Haozhe Pan,Tao Yang.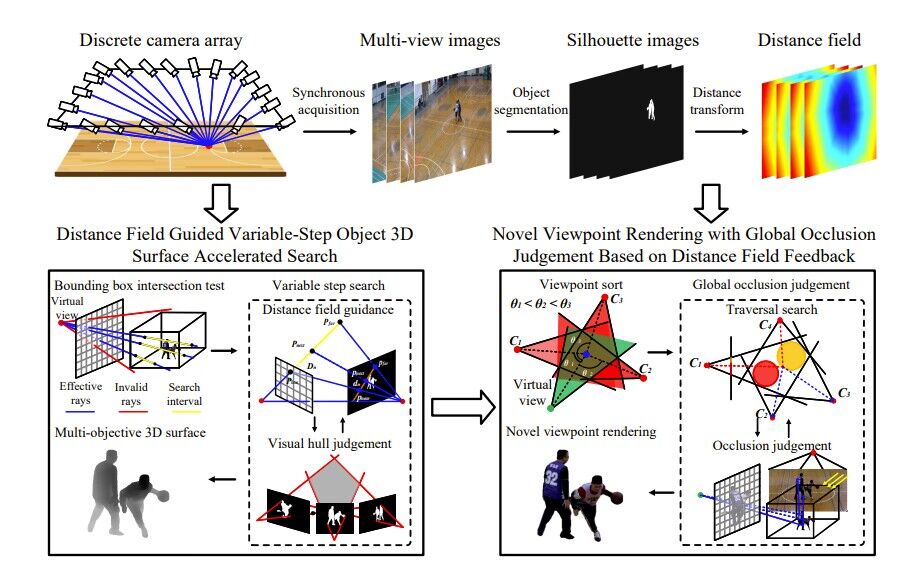
Free-viewpoint video allows the user to view objects from any virtual perspective, creating an immersive visual experience. This technology enhances the interactivity and freedom of multimedia performance. However, many free-viewpoint video synthesis methods are hard to satisfy the requirements of real-time and high precision, particularly in sports competitions with large areas and numerous objects. To address these issues, we propose a free-viewpoint video synthesis method based on distance field acceleration. The central idea is to fuse multi-view distance field information and use it to adjust the search step size adaptively. Adaptive step size search is applied in two aspects: fast estimation of multi-object three-dimensional surfaces and synthetic view rendering based on global occlusion judgement. And we implement parallel computing and interactive display of this method on the CUDA and OpenGL interoperability frameworks. Afterward, we build real-world and simulated experimental platforms to obtain sufficient multi-view image datasets and evaluate the performance of our method. Experimental results show that the proposed method can render freeviewpoint videos with multiple objects in large-scale sports fields at 25 fps. Furthermore, the visual quality of our synthetic novel viewpoint images outperforms state-of-the-art neural-rendering-based methods.
Read MoreScene-Constrained Neural Radiance Fields for High-Quality Sports Scene Rendering Based on Visual Sensor Network
Xiaoshi Zhou ,Yanran Dai ,Haidong Qin ,Shunran Qiu ,Xueyang Liu ,Yujie Dai ,Jing Li, Tao Yang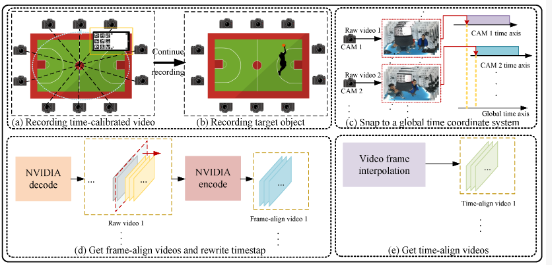
Achieving precise synchronization is critical for multi-camera systems in various applications. Traditional methods rely on hardware-triggered synchronization, necessitating significant manual effort to connect and adjust synchronization cables, especially with multiple cameras involved. This not only increases labor costs but also restricts scene layout and incurs high setup expenses. To address these challenges, we propose a novel subframe synchronization technique for multi-camera systems that operates without the need for additional hardware triggers. Our approach leverages a time-calibrated video featuring specific markers and a uniformly moving ball to accurately extract the temporal relationship between local and global time systems across cameras. This allows for the calculation of new timestamps and precise frame-level alignment. By employing interpolation algorithms, we further refine synchronization to the subframe level. Experimental results validate the robustness and high temporal precision of our method, demonstrating its adaptability and potential for use in demanding multi-camera setups.
Read MoreLD-SLAM: A Robust and Accurate GNSS-Aided Multi-Map Method for Long-Distance Visual SLAM
Dongdong Li, Fangbing Zhang, Jiaxiao Feng, Zhijun Wang, Jinghui Fan, Ye Li, Jing Li, Tao Yang.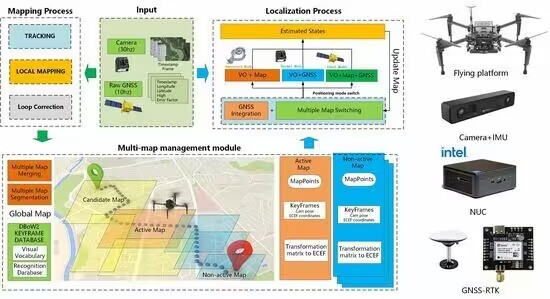
Continuous, robust, and precise localization is pivotal in enabling the autonomous operation of robots and aircraft in intricate environments, particularly in the absence of GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signals. However, commonly employed approaches, such as visual odometry and inertial navigation systems, encounter hindrances in achieving effective navigation and positioning due to issues of error accumulation. Additionally, the challenge of managing extensive map creation and exploration arises when deploying these systems on unmanned aerial vehicle terminals. This study introduces an innovative system capable of conducting long-range and multi-map visual SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) using monocular cameras equipped with pinhole and fisheye lens models. We formulate a graph optimization model integrating GNSS data and graphical information through multi-sensor fusion navigation and positioning technology. We propose partitioning SLAM maps based on map health status to augment accuracy and resilience in large-scale map generation. We introduce a multi-map matching and fusion algorithm leveraging geographical positioning and visual data to address excessive discrete mapping, leading to resource wastage and reduced map-switching efficiency. Furthermore, a multi-map-based visual SLAM online localization algorithm is presented, adeptly managing and coordinating distinct geographical maps in different temporal and spatial domains. We employ a quadcopter to establish a testing system and generate an aerial image dataset spanning several kilometers. Our experiments exhibit the framework’s noteworthy robustness and accuracy in long-distance navigation. For instance, our GNSS-assisted multi-map SLAM achieves an average accuracy of 1.5 m within a 20 km range during unmanned aerial vehicle flights.
Read MoreOnline Ground Multitarget Geolocation Based on 3D Map Construction Using a UAV Platform
Fangbing Zhang, Tao Yang, Yi Bai, Yajia Ning, Ye Li, Jinghui Fan, Dongdong Li.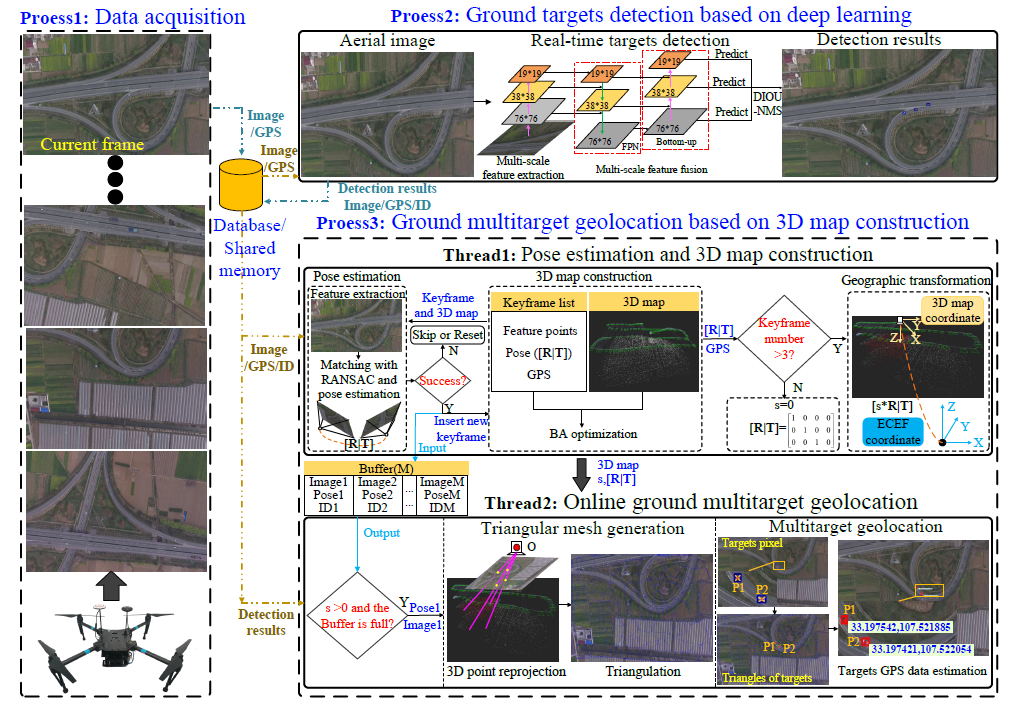
Geolocating multiple targets of interest on the ground from an aerial platform is an important activity in many applications, such as visual surveillance. However, due to the limited measurement accuracy of commonly used airborne sensors (including altimeters, accelerometer, gyroscopes, etc.) and the small size, complex motion, and a large number of ground targets in aerial images, most of the current unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based ground target geolocation algorithms have difficulty obtaining accurate geographic location coordinates online, especially at middle and high altitudes. To solve these problems, in this paper, a novel online ground multitarget geolocation framework using a UAV platform is proposed, which minimizes the introduction of sensor error sources and uses only monocular aerial image sequences and Global Positioning System (GPS) data to perform parallel processing of target detection and rapid three-dimensional (3D) sparse geographic map construction and target geographic location estimations, thereby improving the accuracy and speed of ground multitarget online geolocation. In this framework, a detection algorithm based on deep learning is first adopted to improve the accuracy and robustness of small target detection in aerial images by constructing an aerial image dataset. Then, we propose a novel target geolocation algorithm based on 3D map construction, which combines continuous images and GPS data collected online using a UAV platform to generate a 3D geographic map and accurately estimates the GPS location of the target center pixel through projection and triangulation of the map points on the image. Finally, we design a data transmission architecture that selects multiple processes to perform image acquisition, target detection and target geolocation tasks in parallel and utilizes database communication between the processes to achieve accurate online geolocation of ground targets in aerial images, regardless of whether the target is in a static or moving state. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, we build an online ground multitarget geolocation system using a quad-rotor UAV and carry out a large number of experiments in simulations and real environments. Qualitative and quantitative experimental results proved that the framework can accurately locate ground targets in various complex environments, such as parks, highways, schools, cities, different flight altitudes (50–2000m) and different attitude angles, and the average positioning error is approximately 1 m at 2000 m for cities with rich 3D structures.
Read MoreCalibration-Free Cross-Camera Target Association Using Interaction Spatiotemporal Consistency
Congcong Li;Jing Li;Yuguang Xie;Jiayang Nie;Tao Yang;Zhaoyang Lu.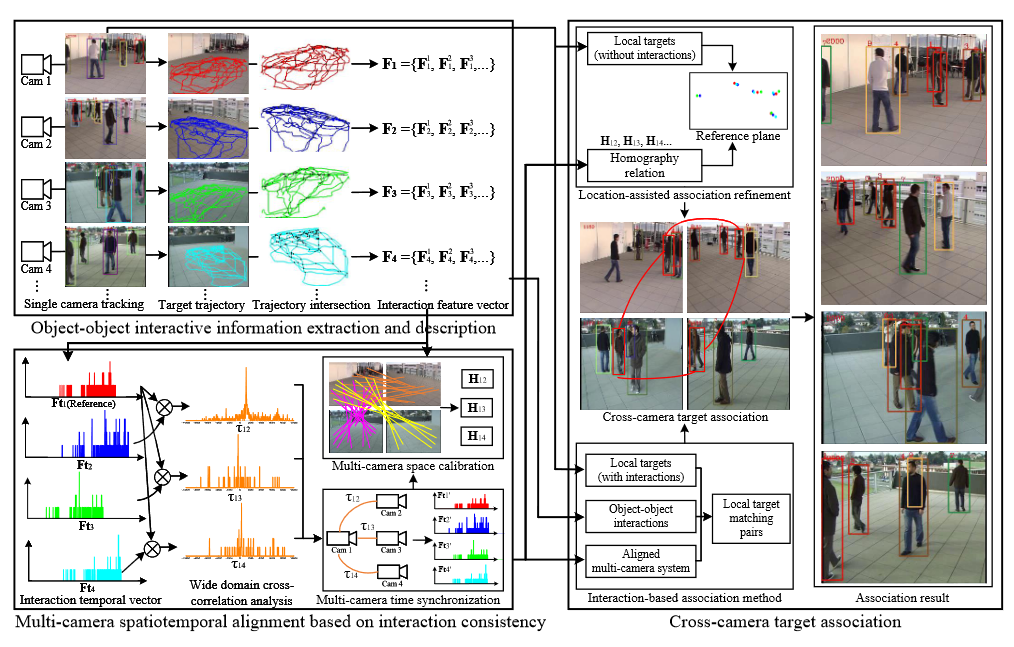
In this paper, we propose a novel calibration-free cross-camera target association algorithm that aims to relate local visual data of the same object across cameras with overlapping FOVs. Unlike other methods using object's own characteristics, our approach makes full use of the interactions between objects and explores their spatiotemporal consistency in projection transformation to associate cameras. It has wider applicability in deployed overlapping multi-camera systems with unknown or rarely available calibration data, especially if there is a large perspective gap between cameras. Specifically, we first extract trajectory intersection which is one of the typical object-object interactive behaviors from each camera for feature vector construction. Then, based on the consistency of object-object interactions, we propose a multi-camera spatiotemporal alignment method via wide-domain cross-correlation analysis. It realizes time synchronization and spatial calibration of the multi-camera system simultaneously. After that, we introduce a cross-camera target association approach using aligned object-object interactions. The local data of the same target are successfully associated across cameras without any additional calibration. Extensive experimental evaluations on different databases verify the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed method.
Read MoreTime Series Fusion-based Multi-camera Self-calibration For Free-view Video Generation in Low-texture Sports Scene
Feng Zhou, Jing Li,Yanran Dai, Lichen Liu, Haidong Qin, Yuqi Jiang, Shikuan Hong, Bo Zhao, Tao Yang.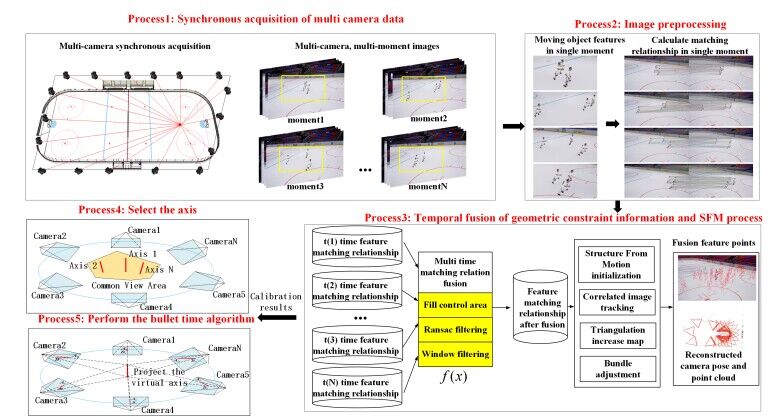
Multicamera calibration is an important technique for generating free-view video. By arranging multiple cameras in a scene after camera calibration and image processing, a multidimensional viewing experience can be presented to the audience. To address the problem that low texture cannot be robustly self-calibrated in common sports scenes when placing artificial markers or towers in the calibration process is impractical, this article proposes a robust multicamera calibration method based on sequence feature matching and fusion. Additionally, to validate the effectiveness of the proposed calibration algorithm, a virtual axis fast bullet-time synthesis algorithm is proposed for generating a free-view video. First, camera self-calibration is performed in low-texture situations by fusing dynamic objects in time series to enrich geometric constraints in scenes without the use of calibration panels or additional artificial markers. Second, a virtual-axis bullet-time video synthesis method based on the calibration result is proposed. In the calibrated multicamera scenario, a fast bullet-time video is generated by constructing a virtual axis. Qualitative and quantitative experiments in comparison with a state-of-the-art calibration method demonstrate the validity and robustness of the proposed calibration algorithm for free-view video synthesis tasks.
Read MoreBullet-time Video Synthesis Based on Virtual Dynamic Target Axis
Haidong Qin, Jing Li, Yuqi Jiang, Yanran Dai, Shikuan Hong, Feng Zhou, Zhijun Wang, Tao Yang.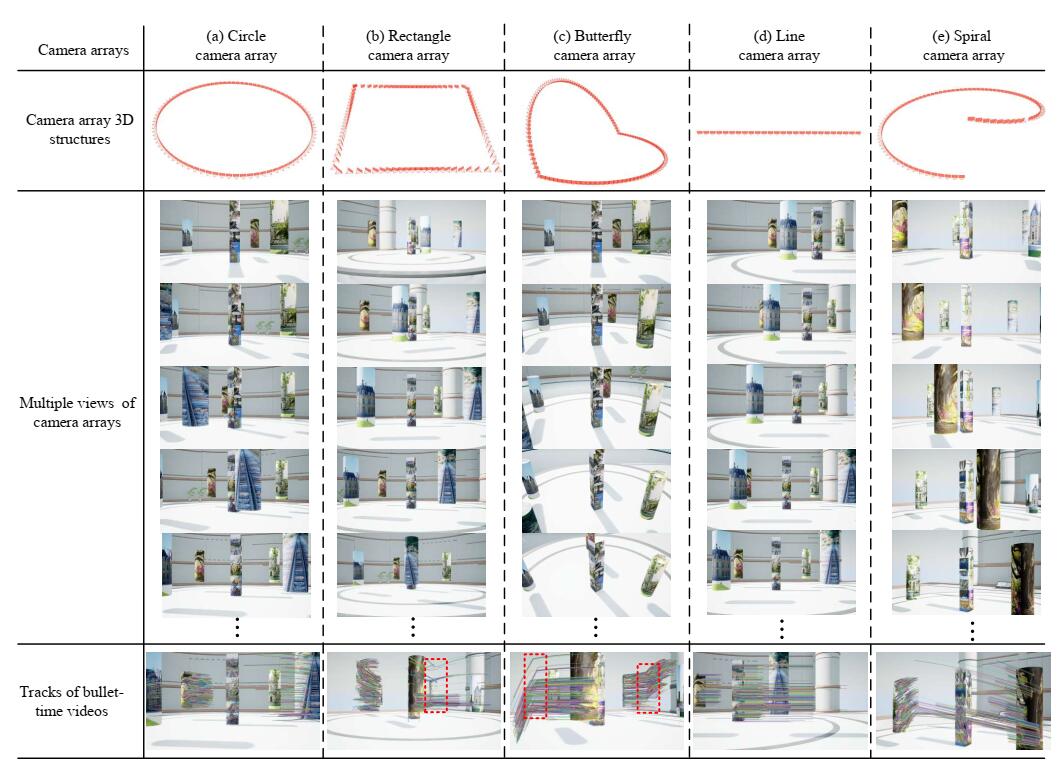
Bullet-time videos have been widely used in movies, TV advertisements, and computer games, and can produce an immersive and smooth orbital free-viewpoint of frozen action. However, existing bullet-time video synthesis methods remain challenging in practical applications, especially in complex situations with poor camera calibration and a variety of camera array structures. This paper proposes a novel bullet-time video synthesis method based on a virtual dynamic target axis. We adopt an image similarity transformation strategy to eliminate image distortion in the bullet-time video. We use a high-order polynomial curve fitting strategy to reserve more bullet-time video frame content. The proposed dynamic target axis strategy can support various camera array structures, including camera arrays with and without a common field of view. In addition, this strategy can also tolerate poor camera calibration situations with unevenly distributed reprojection errors to some extent and synthesize smooth bullet-time videos without high-precision camera calibration. Qualitative and quantitative experiments in real environments and on simulation platforms demonstrate the high performance of our bullet-time video synthesis method. Compared with the state-of-the-art methods, the proposed method shows superiority.
Read MoreImage-only Real-time Incremental UAV Image Mosaic for Multi-strip Flight
Fangbing Zhang, Tao Yang, LinFeng Liu, Bang Liang, Yi Bai, Jing Li.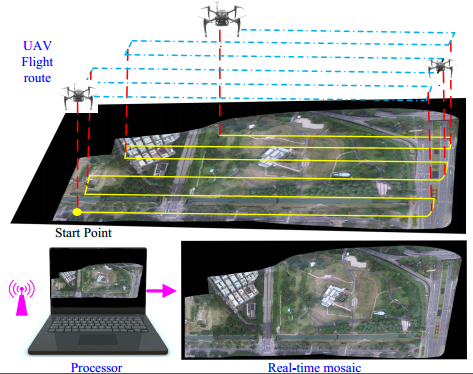
Limited by aircraft flight altitude and camera parameters, it is necessary to obtain wide-angle panoramas quickly by stitching aerial images, which is helpful in rapid disaster investigation, recovery after earthquakes, and battlefield reconnaissance. However, most existing stitching algorithms do not meet practical real-time, robustness, and accuracy requirements simultaneously, especially in the case of a long-distance multi-strip flight. In this paper, we propose a novel image-only real-time UAV image mosaic framework for long-distance multi-strip flights, which does not require any auxiliary information such as GPS or GCPs...
Read MoreMulti-camera Joint Spatial Self-organization for Intelligent Interconnection Surveillance
Congcong Li, Jing Li , Yuguang Xie, Jiayang Nie, Tao Yang, Zhao yang Lu.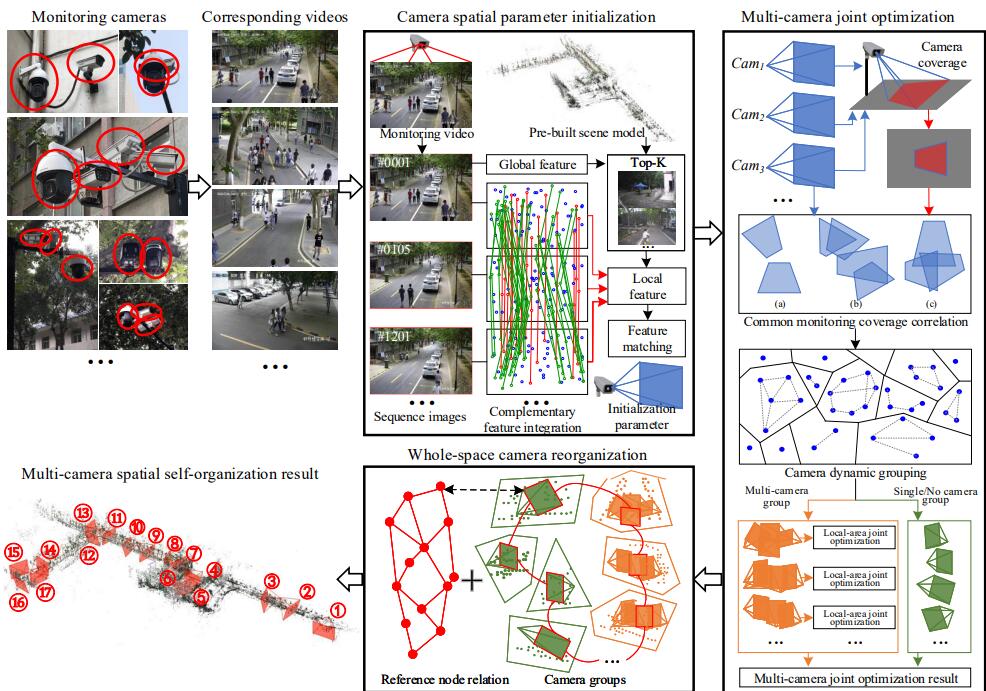
The construction of smart city makes information interconnection play an increasingly important role in intelligent surveillance systems. Especially the interconnection among massive cameras is the key to realizing the evolution from current fragmented monitoring to interconnection surveillance. However, it remains a challenging problem in practical systems due to large sensor quantity, various camera types, and complex spatial layout. Aimed at this problem, this paper proposes a novel multi-camera joint spatial self-organization approach, which realizes interconnection surveillance by unifying cameras into one imaging space. Differing from existing back-end data association strategy, our method takes front-end data calibration as a breakthrough to relate surveillance data ...
Read MoreA Monocular Visual Odometry Method Based on Virtual-Real Hybrid Map in Low-Texture Outdoor Environment
Xiuchuan Xie, TaoYang, Yajia Ning, Fangbing Zhang, Yanning Zhang.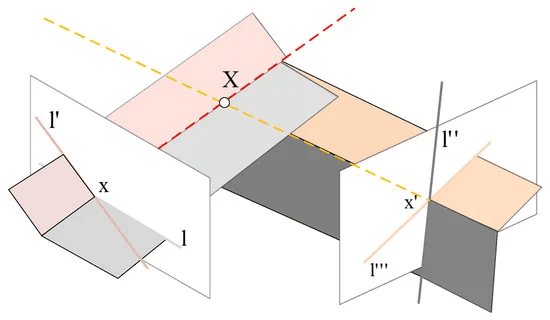
With the extensive application of robots, such as unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in exploring unknown environments, visual odometry (VO) algorithms have played an increasingly important role. The environments are diverse, not always textured, or low-textured with insufficient features, making them challenging for mainstream VO. However, for low-texture environment, due to the structural characteristics of man-made scene, the lines are usually abundant. In this paper, we propose a virtual-real hybrid map based monocular visual odometry algorithm. The core idea is that we reprocess line segment features to generate the virtual intersection matching points, which can be used to build the virtual map. Introducing virtual map can improve the stability of the visual odometry algorithm in low-texture environment. Specifically, we first combine unparallel matched line segments to generate virtual intersection matching points, then, based on the virtual intersection matching points, we triangulate to get a virtual map, combined with the real map built upon the ordinary point features to form a virtual-real hybrid 3D map. Finally, using the hybrid map, the continuous camera pose estimation can be solved. Extensive experimental results have demonstrated the robustness and effectiveness of the proposed method in various low-texture scenes ...
Read MoreUAV-Assisted Wide Area Multi-Camera Space Alignment Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Map
Jing Li, Yuguang Xie, Congcong Li, Yanran Dai, Jiaxin Ma, Zheng Dong, Tao Yang.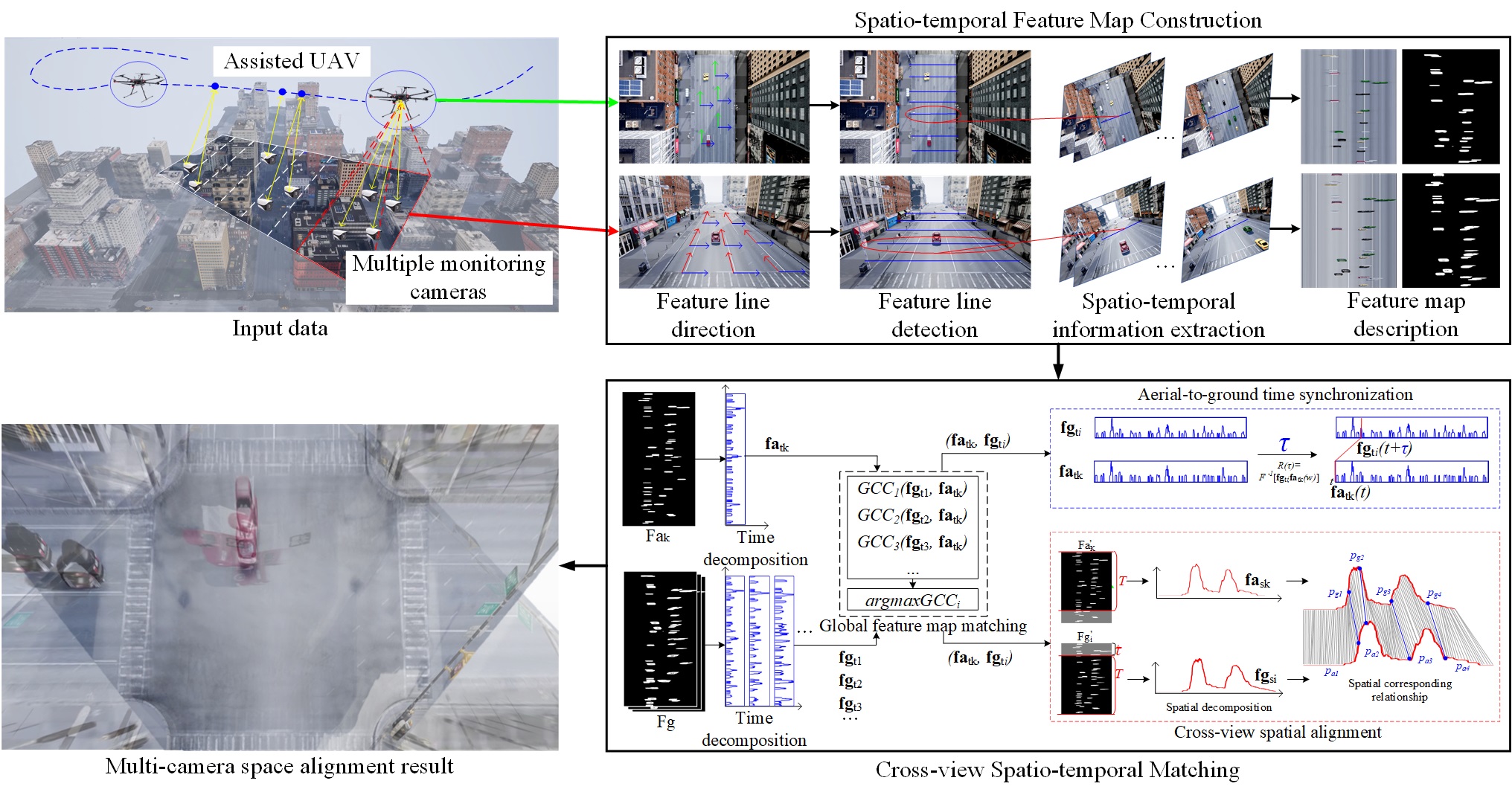
In this paper, we investigate the problem of aligning multiple deployed camera into one united coordinate system for cross-camera information sharing and intercommunication. However, the difficulty is greatly increased when faced with large-scale scene under chaotic camera deployment. To address this problem, we propose a UAV-assisted wide area multi-camera space alignment approach based on spatiotemporal feature map. It employs the great global perception of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to meet the challenge from wide-range environment. Concretely, we first present a novel spatiotemporal feature map construction approach to ...
Read MoreAccurate localization of moving objects in dynamic environment for small UAV platform using global averaging
Xiuchuan Xie, Tao Yang, Yanning Zhang, Bang Liang and Linfeng Liu.
Abstract: In recent years, small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have rapidly developed and are widely used in disaster relief, traffic monitoring and military surveillance. In order to better perform these tasks, it is necessary to improve the environmental perception ability of UAV in dynamic environment including static and dynamic perception ability. Specifically, 3D reconstruction for static scene and localization for moving object are both required. Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) technology has made great progress in static scene structure reconstruction and UAV self motion estimation. However, accurate real-time localization of ...
Read MoreData-Driven Variable Synthetic Aperture Imaging Based on Semantic Feedback
CongCong Li, Jing Li, Yanran Dai, Tao Yang, Yuguang Xie, Zhaoyang Lu.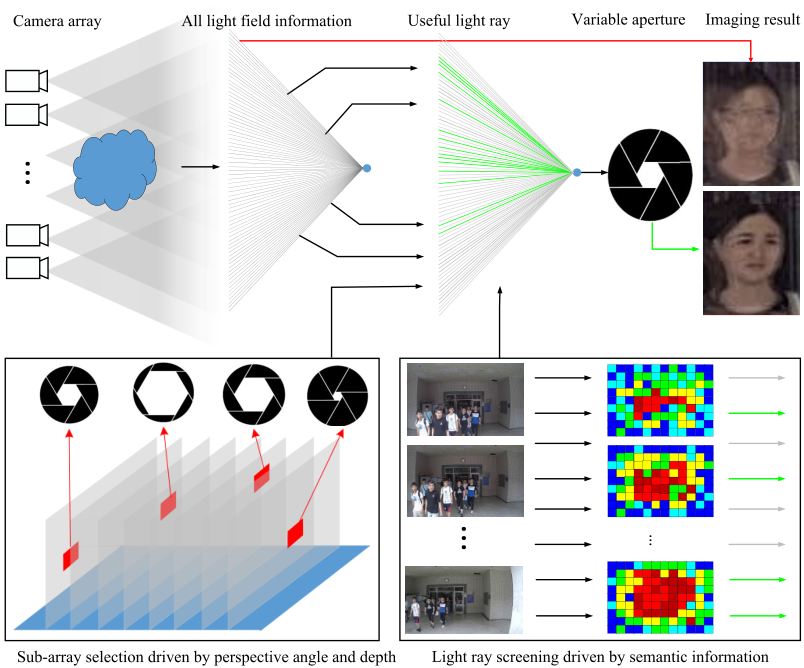
Synthetic aperture imaging, which has been proved to be an effective approach for occluded object imaging, is one of the challenging problems in the field of computational imaging. Currently most of the related researches focus on fixed synthetic aperture which usually accompanies with mixed observation angle and foreground de-focus blur. But the existence of them is frequently a source of perspective effect decrease and occluded object imaging quality degradation. In order to solve this problem, we propose a novel data-driven variable synthetic aperture imaging based on semantic feedback...
Read MoreMultiple-Object-Tracking Algorithm Based on Dense Trajectory Voting in Aerial Videos
Tao Yang, Dongdong Li, Yi Bai, Fangbing Zhang, Sen Li, Miao Wang, Zhuoyue Zhang, Jing Li.In recent years, UAV technology has developed rapidly. Due to the mobility, low cost, and variable monitoring altitude of UAVs, multiple-object detection and tracking in aerial videos has become a research hotspot in the field of computer vision. However, due to camera motion, small target size, target adhesion, and unpredictable target motion, it is still difficult to detect and track targets of interest in aerial videos, especially in the case of a low frame rate where the target position changes too much. In this paper, we propose a multiple-object-tracking algorithm based on dense-trajectory voting in aerial videos...
Read MoreAn Adaptive Framework for Multi-Vehicle Ground Speed Estimation in Airborne Videos
Jing Li, Shuo Chen, Fangbing Zhang, Erkang Li ,Tao Yang, Zhaoyang Lu.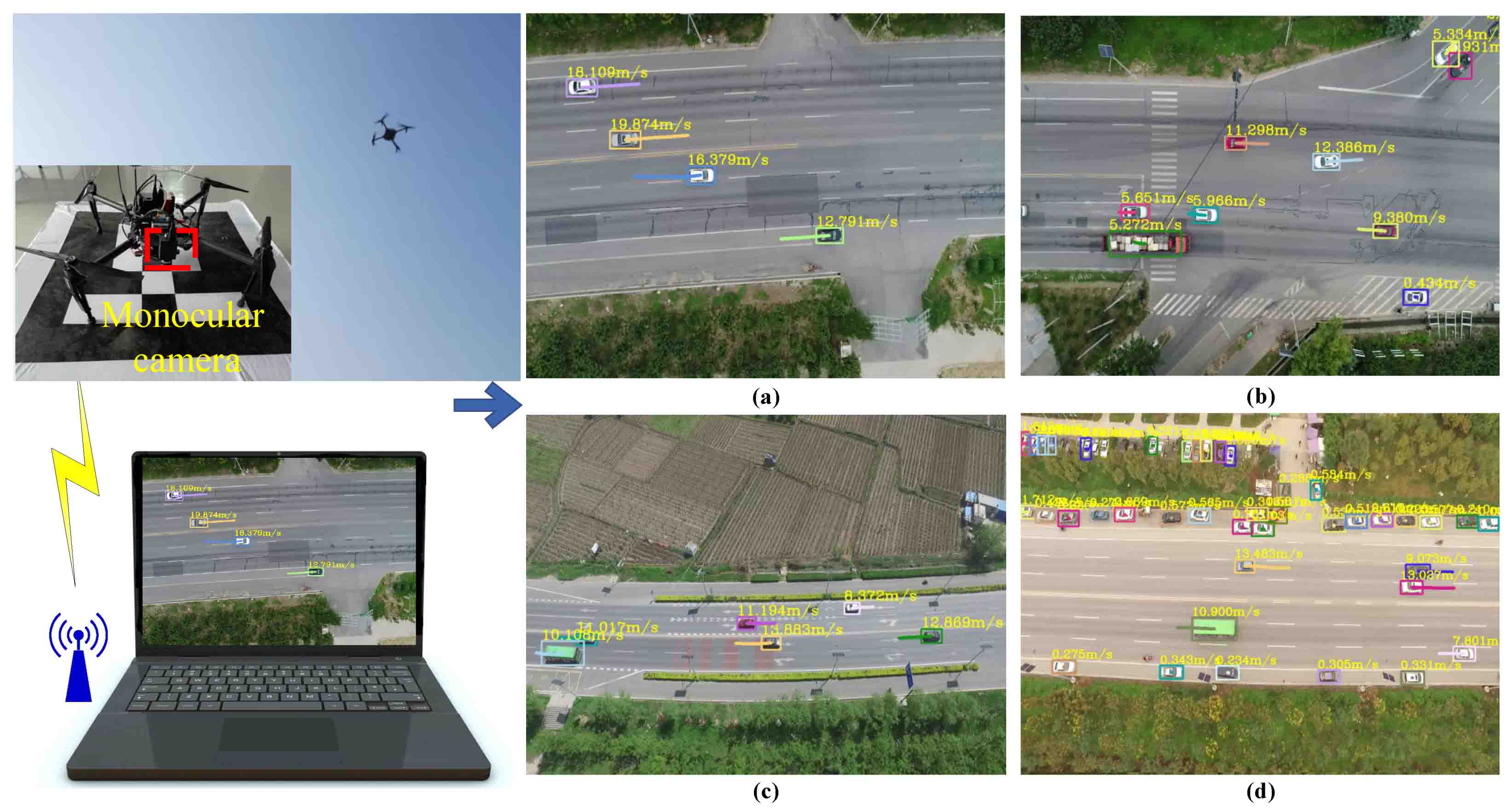
With the rapid development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), UAV-based intelligent airborne surveillance systems represented by real-time ground vehicle speed estimation have attracted wide attention from researchers. However, there are still many challenges in extracting speed information from UAV videos, including the dynamic moving background, small target size, complicated environment, and diverse scenes. In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive framework for multi-vehicle ground speed estimation in airborne videos. Firstly, we build a traffic dataset based on UAV...
Read MoreJoint Deep and Depth for Object-level Segmentation and Stereo Tracking in Crowds
Jing Li, Lisong Wei, Fangbing Zhang, Tao Yang, Zhaoyang Lu.Tracking multiple people in crowds is a fundamental and essential task in the multimedia field. It is often hindered by difficulties such as dynamic occlusion between objects, cluttered background and abrupt illumination changes. To respond to this need, in this paper, we combine deep and depth to build a stereo tracking system for crowds. The core of the system is the fusion of the advantages of deep learning and depth information, which is exploited to achieve object segmentation and improve the multiobject tracking performance in severe occlusion...
Read MorePanoramic UAV Surveillance and Recycling System based on Structure-free Camera Array
Tao Yang , Zhi Li , Fangbing Zhang , Bolin Xie , Jing Li , Linfeng Liu.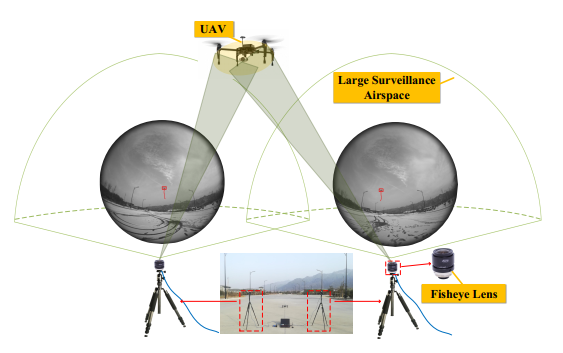
In recent years, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have rapidly developed, but the illegal use of UAVs by civilians has resulted in disorder and security risks and has increasingly triggered community concern and worry. Therefore, the monitoring and recycling of UAVs in key regions is of great significance. This paper presents a novel panoramic UAV surveillance and autonomous recycling system that is based on an unique structure-free fisheye camera array and has the capability of real-time UAV detection...
Read MoreHierarchical Clustering-Aligning Framework Based Fast Large-Scale 3D Reconstruction Using Aerial Imagery
Xiuchuan Xie, Tao Yang, Dongdong Li, Zhi Li, Yanning Zhang.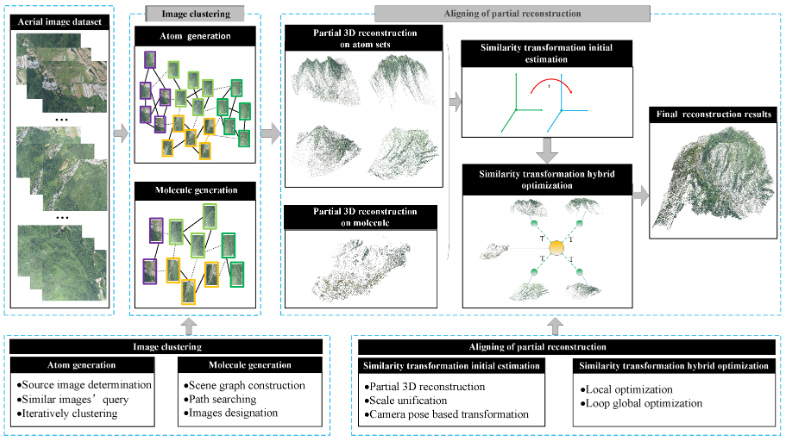
With extensive applications of Unmanned Aircraft Vehicle (UAV) in the field of remote sensing, 3D reconstruction using aerial images has been a vibrant area of research. However, fast large-scale 3D reconstruction is a challenging task. For aerial image datasets, large scale means that the number and resolution of images are enormous, which brings significant computational cost to the 3D reconstruction, especially in the process of Structure from Motion (SfM). In this paper, for fast large-scale SfM, we propose a clustering-aligning framework that hierarchically merges partial structures...
Read MoreVisual Detail Augmented Mapping for Small Aerial Target Detection
Jing Li,Yanran Dai,Congcong Li, Junqi Shu, Dongdong Li, Tao Yang,Zhaoyang Lu.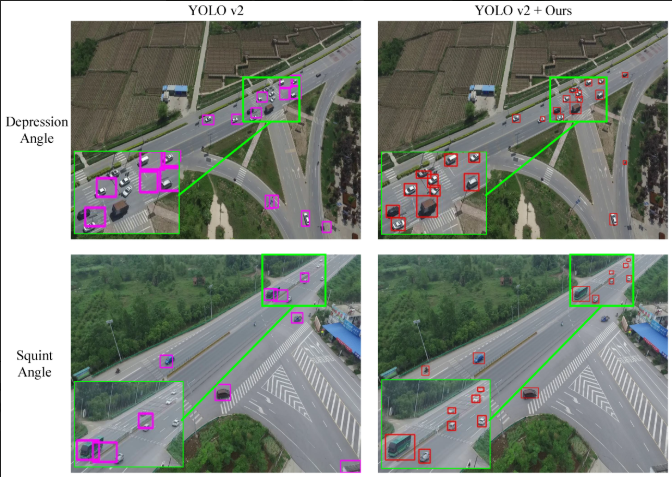
Moving target detection plays a primary and pivotal role in avionics visual analysis, which aims to completely and accurately detect moving objects from complex backgrounds. However, due to the relatively small sizes of targets in aerial video, many deep networks that achieve success in normal size object detection are usually accompanied by a high rate of false alarms and missed detections. To address this problem, we propose a novel visual detail augmented mapping approach for small aerial target detection. Concretely, we first present a multi-cue foreground segmentation algorithm including motion and grayscale information to extract potential regions...
Read MoreHybrid Camera Array-Based UAV Auto-Landing on Moving UGV in GPS-Denied Environment
Tao Yang, Qiang Ren,Fangbing Zhang ,Bolin Xie, Hailei Ren, Jing Li,Yanning Zhang.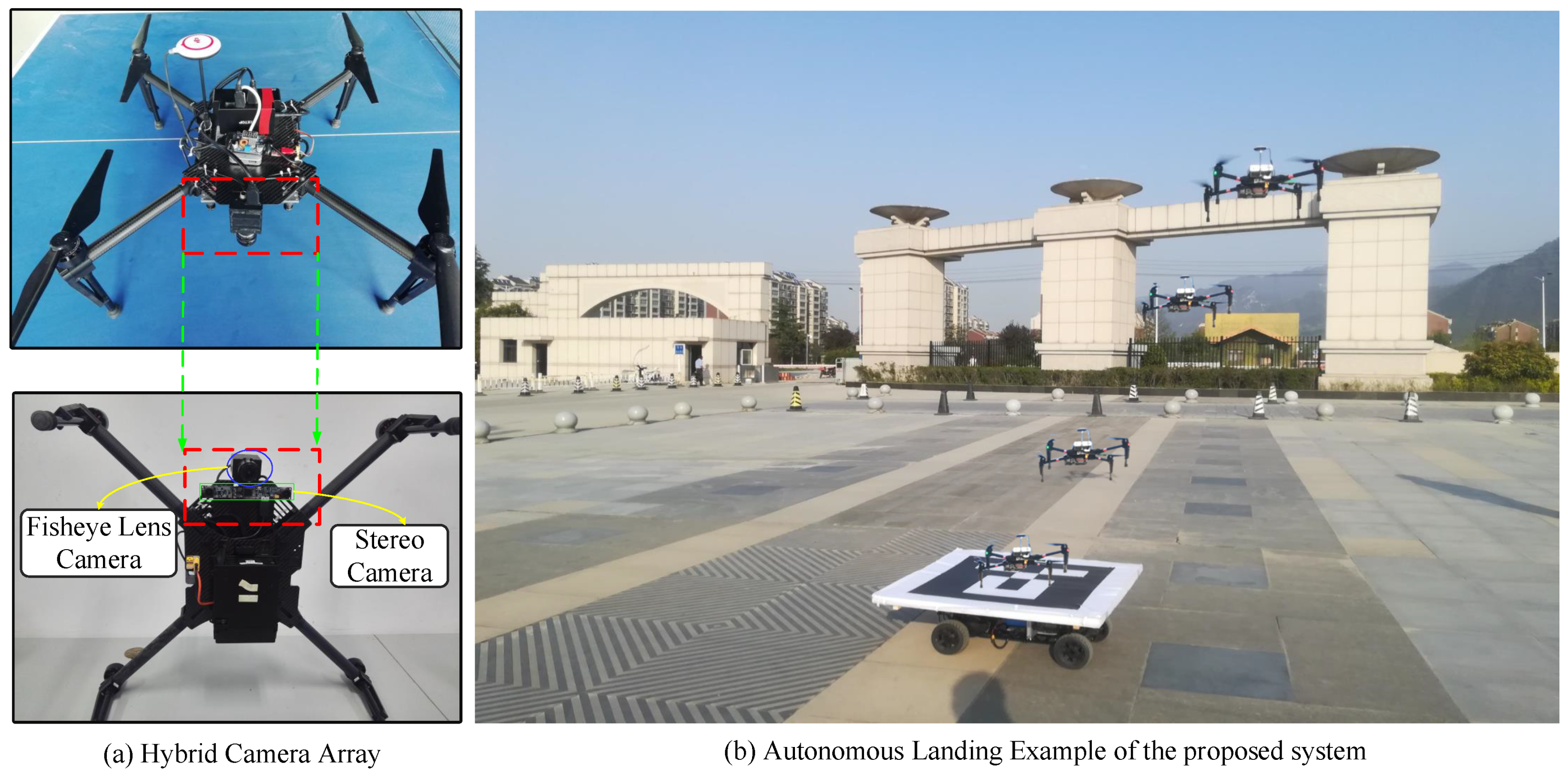
With the rapid development of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) systems, the autonomous landing of a UAV on a moving Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) has received extensive attention as a key technology. At present, this technology is confronted with such problems as operating in GPS-denied environments, a low accuracy of target location, the poor precision of the relative motion estimation, delayed control responses, slow processing speeds, and poor stability. To address these issues, we present a hybrid camera array-based autonomous landing UAV that can land on a moving UGV in a GPS-denied environment...
Read MoreHierarchically Learned View-Invariant Representations for Cross-View Action Recognition
Yang Liu, Zhaoyang Lu, Jing Li, Tao Yang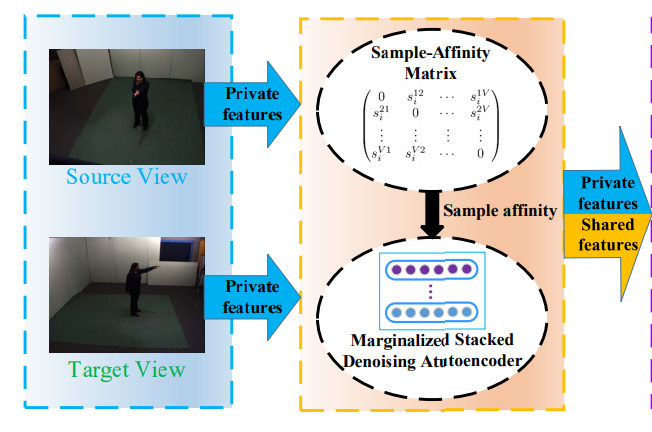
Recognizing human actions from varied views is challenging due to huge appearance variations in different views. The key to this problem is to learn discriminant view-invariant representations generalizing well across views. In this paper, we address this problem by learning view-invariant representations hierarchically using a novel method, referred to as Joint Sparse Representation and Distribution Adaptation (JSRDA).. . .
Read MoreA Hierarchical Association Framework for Multi-Object Tracking in Airborne Videos
Ting Chen, Andrea Pennisi, Zhi Li, Yanning Zhang, Hichem SahliMulti-Object Tracking (MOT) in airborne videos is a challenging problem due to the uncertain airborne vehicle motion, vibrations of the mounted camera, unreliable detections, changes of size, appearance and motion of the moving objects and occlusions caused by the interaction between moving and static objects in the scene. To deal with these problems. . .
Read MoreMonocular Vision SLAM-Based UAV Autonomous Landing in Emergencies and Unknown Environments
Tao Yang, Peiqi Li, Huiming Zhang, Jing Li, Zhi Li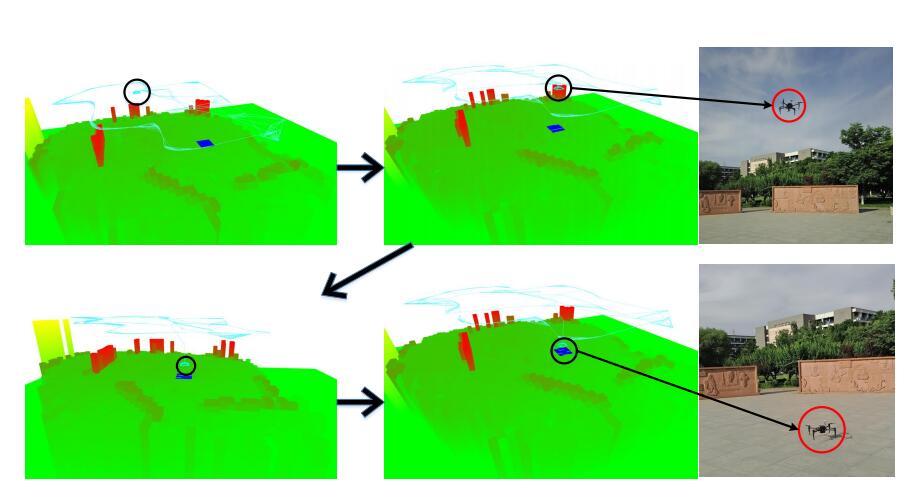
With the popularization and wide application of drones in military and civilian fields, the safety of drones must be considered. At present, the failure and drop rates of drones are still much higher than those of manned aircraft. Therefore, it is imperative to improve the research on the safe landing and recovery of drones. However, most drone navigation methods rely on global positioning system (GPS) signals. . .
Read MoreReal-Time Ground Vehicle Detection in Aerial Infrared Imagery Based on Convolutional Neural Network
Xiaofei Liu, Tao Yang, and Jing Li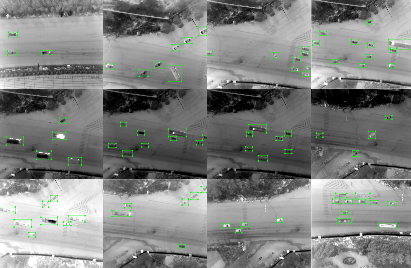
An infrared sensor is a commonly used imaging device. Unmanned aerial vehicles, the most promising moving platform, each play a vital role in their own field, respectively. However, the two devices are seldom combined in automatic ground vehicle detection tasks. Therefore, how to make full use of them—especially in ground vehicle detection based on aerial imagery–has aroused wide academic concern. . .
Read MoreGlobal Temporal Representation Based CNNs for Infrared Action Recognition
Yang Liu, Zhaoyang Lu, Jing Li, Tao Yang, Chao Yao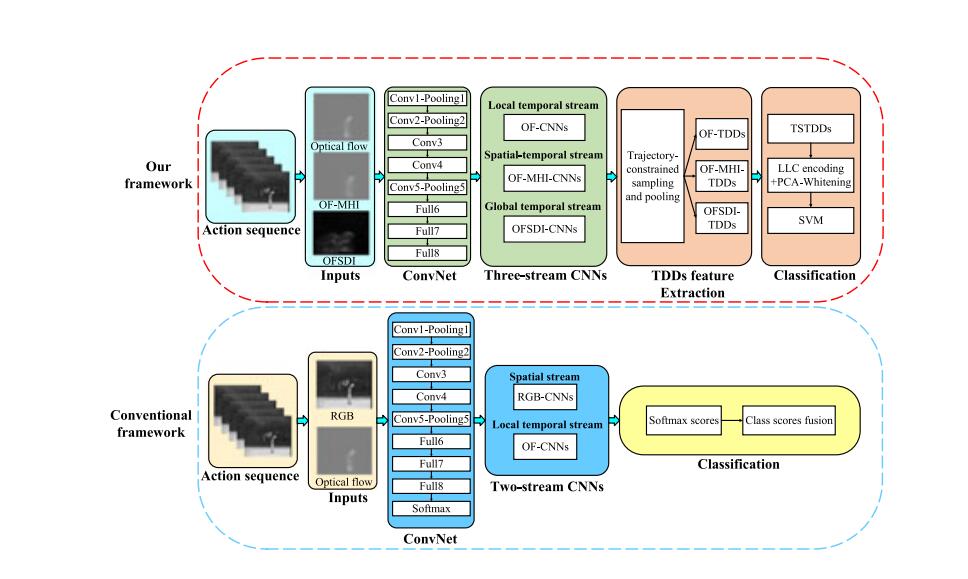
Infrared human action recognition has many advantages, i.e., it is insensitive to illumination change, appearance variability, and shadows. Existing methods for infrared action recognition are either based on spatial or local temporal information, however, the global temporal information, which can better describe the movements of body parts across the whole video. . .
Read MoreCross-domain Co-occurring Feature for Visible-infrared Image Matching
Jing Li, Congcong Li, Tao Yang, Zhaoyang Lu.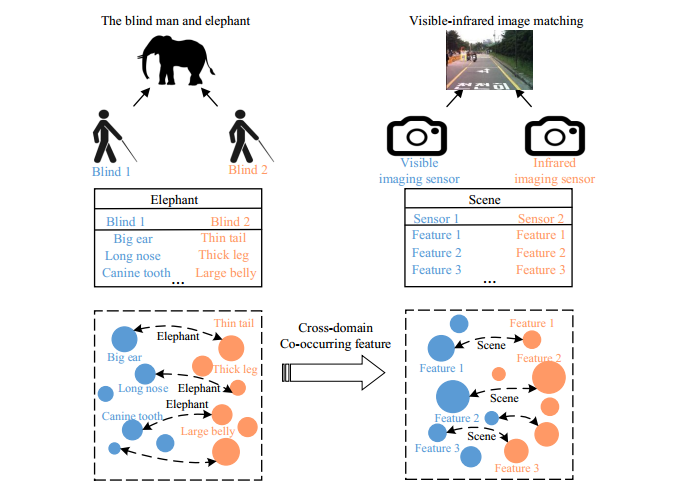
As the two most commonly used imaging devices, infrared sensor and visible sensor play a vital and essential role in the field of heterogeneous image matching. Therefore, visible-infrared image matching which aims to search images across them has important application and theoretical significance. However, due to the vastly different imaging principles, how to accurately match between visible and infrared image remains a challenge. . .
Read MoreImproved compressive tracking based on pixelwise learner
Ting Chen, Hichem Sahli, Yanning Zhang, Tao Yang.This work expands upon state-of-the-art multiscale tracking based on compressive sensing (CT) by increasing the overall tracking accuracy. A pixelwise classification stage is incorporated in the CT-based tracker to obtain a relatively stable appearance model, by distinguishing object pixels from the background. .
Read MoreNighttime Foreground Pedestrian Detection Based on Three-Dimensional Voxel Surface Model
Jing Li 1,*, Fangbing Zhang 1, Lisong Wei 1, Tao Yang 2,*Orcid and Zhaoyang Lu 1.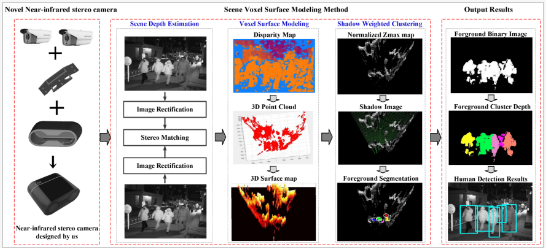
Pedestrian detection is among the most frequently-used preprocessing tasks in many surveillance application fields, from low-level people counting to high-level scene understanding. Even though many approaches perform well in the daytime with sufficient illumination, pedestrian detection at night is still a critical and challenging problem for video surveillance systems. .
Read MoreA Novel Visual Vocabulary Translator based Cross-domain Image Matching
Jing Li, Congcong Li, Tao Yang, Zhaoyang Lu.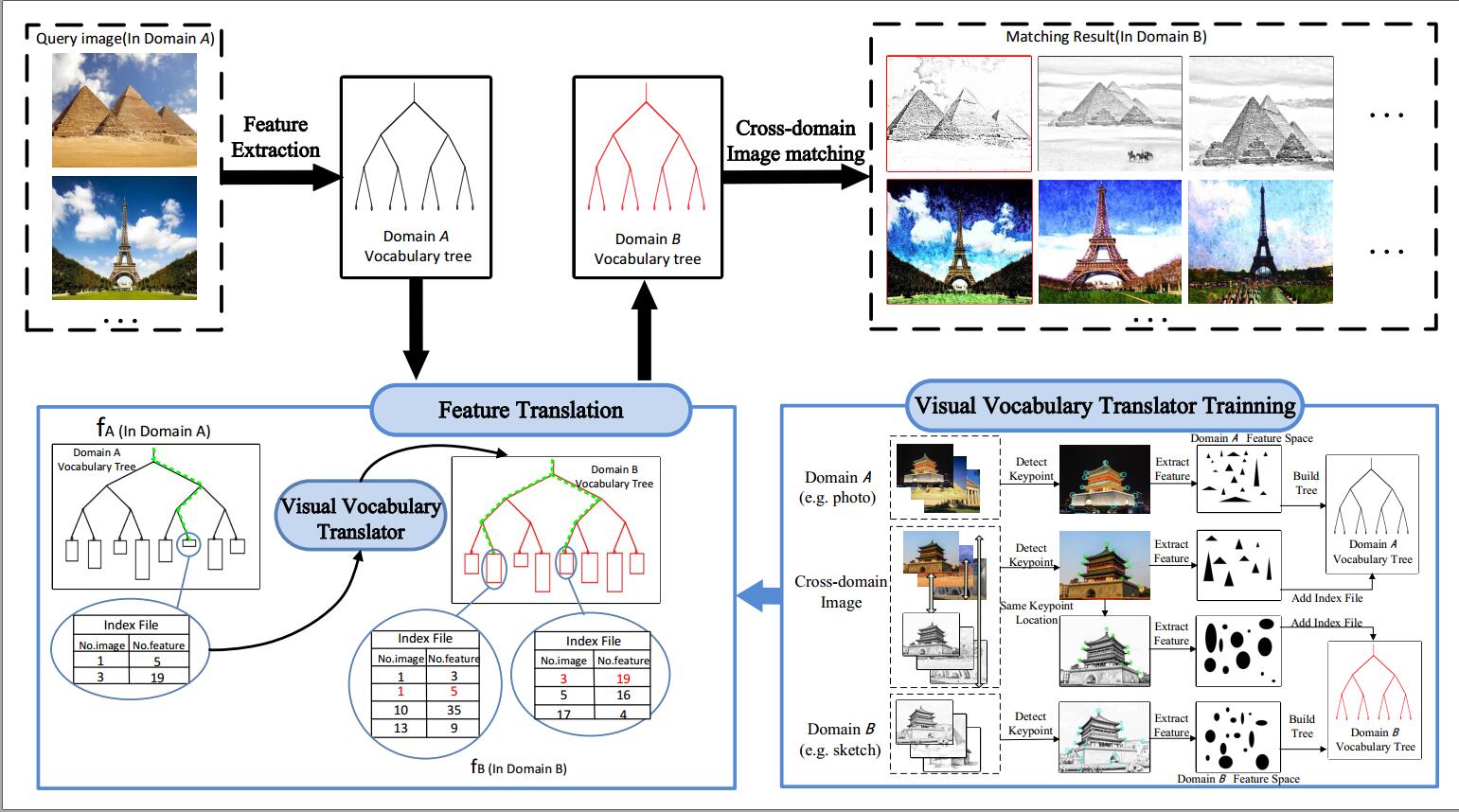
Cross-domain image matching, which investigates the problem of searching images across different visual domains such as photo, sketch or painting, has attracted intensive attention in computer vision due to its widespread application. Unlike intra-domain matching, cross-domain images appear quite different in various characteristics.
Read MoreRandom sampling and model competition for guaranteed multiple consensus sets estimation
Jing Li, Tao Yang, Jingyi Yu.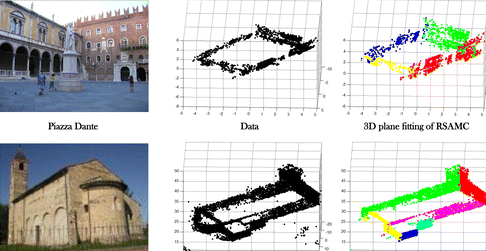
Robust extraction of consensus sets from noisy data is a fundamental problem in robot vision. Existing multimodel estimation algorithms have shown success on large consensus sets estimations. One remaining challenge is to extract small consensus sets in cluttered multimodel data set. In this article, we present an effective multimodel extraction method to solve this challenge.
Read MoreSynthetic Aperture Photography using a Moving Camera-IMU System
Xiaoqiang Zhang, Yanning Zhang, Tao Yang, Yee-Hong Yang.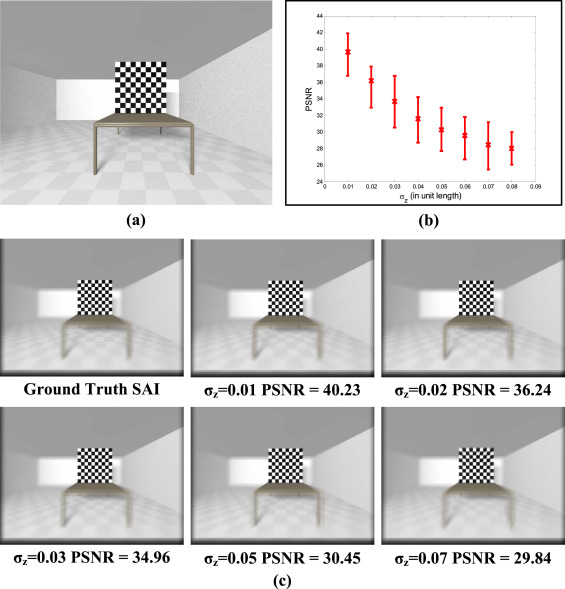
Occlusion poses as a critical challenge in computer vision for a long time. Recently, the technique of synthetic aperture photography using a camera array has been regarded as a promising way to address the problem of occluded object imaging. Unfortunately, the expensive cost of a standard camera array system with the required calibration procedure still limits the widespread popularity of this technique.
Read MoreConvolutional Neural Network-Based Robot Navigation Using Uncalibrated Spherical Images
Lingyan Ran, Yanning Zhang, Qilin Zhang, Tao Yang.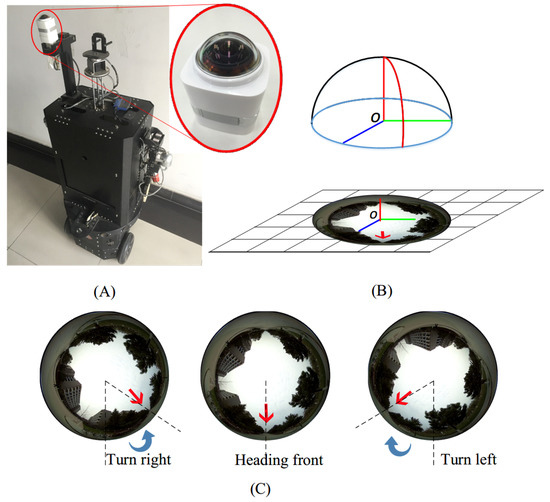
Vision-based mobile robot navigation is a vibrant area of research with numerous algorithms having been developed, the vast majority of which either belong to the scene-oriented simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) or fall into the category of robot-oriented lane-detection/trajectory tracking. These methods suffer from high computational cost and require stringent labelling and calibration efforts.
Read MoreKinect based real-time synthetic aperture imaging through occlusion
TaoYang, Wenguang Ma, Sibing Wang, JingLi, Jingyi Yu, Yanning Zhang.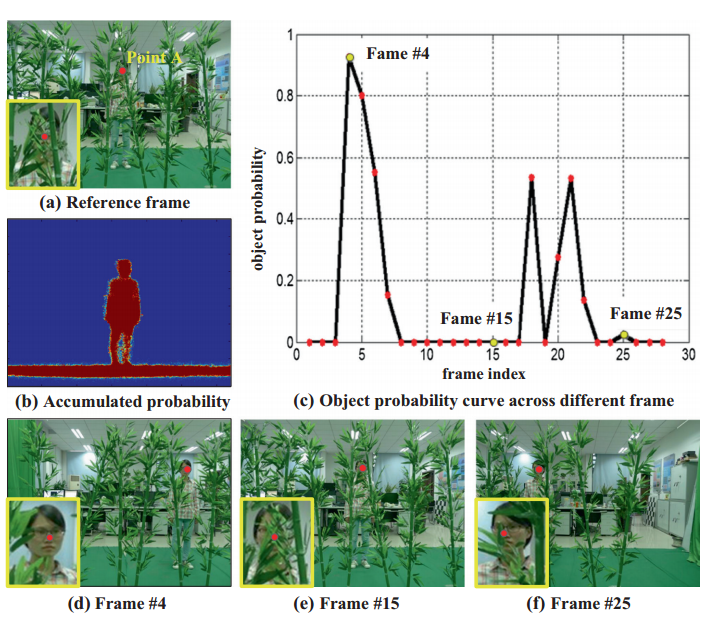
Real-time and high performance occluded object imaging is a big challenge to many computer vision applications. In recent years, camera array synthetic aperture theory proves to be a potential powerful way to solve this problem.
Read MoreA Ground-Based Near Infrared Camera Array System for UAV Auto-Landing in GPS-Denied Environment
Tao Yang, Guangpo Li, Jing Li, Yanning Zhang, Xiaoqiang Zhang, Zhuoyue Zhang, Zhi Li.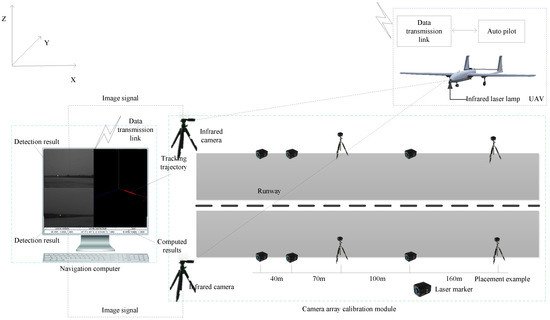
This paper proposes a novel infrared camera array guidance system with capability to track and provide real time position and speed of a fixed-wing Unmanned air vehicle (UAV) during a landing process. The system mainly include three novel parts: (1) Infrared camera array and near infrared laser lamp based cooperative long range optical imaging module;
Read MoreTracking with dynamic weighted compressive model
Ting Chen, Yanning Zhang, Tao Yang, Hichem Sahli. J.Fast compressive tracking utilizes a very sparse measurement matrix to capture the appearance model of targets. Such model performs well when the tracked targets are well defined. However, when the targets are low-grain, low-resolution, or small, a single fixed size sparse measurement matrix is not sufficient enough to preserve the image structure of the target.
Read MoreSmall Moving Vehicle Detection in a Satellite Video of an Urban Area
Tao Yang, Xiwen Wang, Bowei Yao, Jing Li, Yanning Zhang, Zhannan He, Wencheng Duan.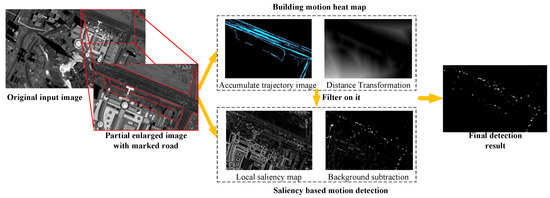
Vehicle surveillance of a wide area allows us to learn much about the daily activities and traffic information. With the rapid development of
Diverse Scene Stitching from a Large-Scale Aerial Video Dataset
TaoYang, JingLi, Jingyi Yu, Sibing Wang, Yanning Zhang,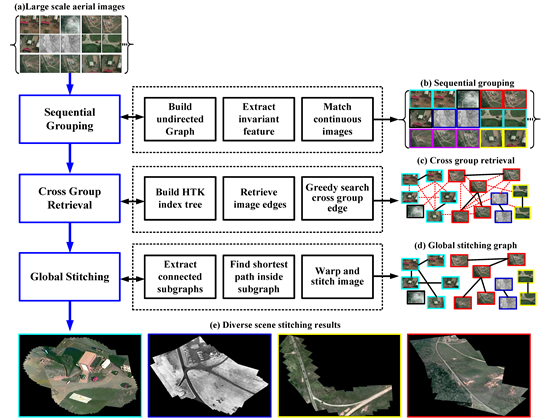
Diverse scene stitching is a challenging task in aerial video surveillance. This paper presents a hybrid stitching method based on the observation that aerial videos captured in real surveillance settings are neither totally ordered nor completely unordered.
Read MoreMultiple-Layer Visibility Propagation-Based Synthetic Aperture Imaging through Occlusion
TaoYang, JingLi, Jingyi Yu, Yanning Zhang,WenguangMa, Xiaomin Tong, RuiYu,Lingyan Ran,
Heavy occlusions in cluttered scenes impose significant challenges to many computer vision applications. Recent light field imaging systems provide new see-through capabilities through synthetic aperture imaging (SAI) to overcome the occlusion problem.
Read MoreMulti-Model Estimation Based Moving Object Detection for Aerial Video
Yanning Zhang, Xiaomin Tong, TaoYang, Wenguang Ma,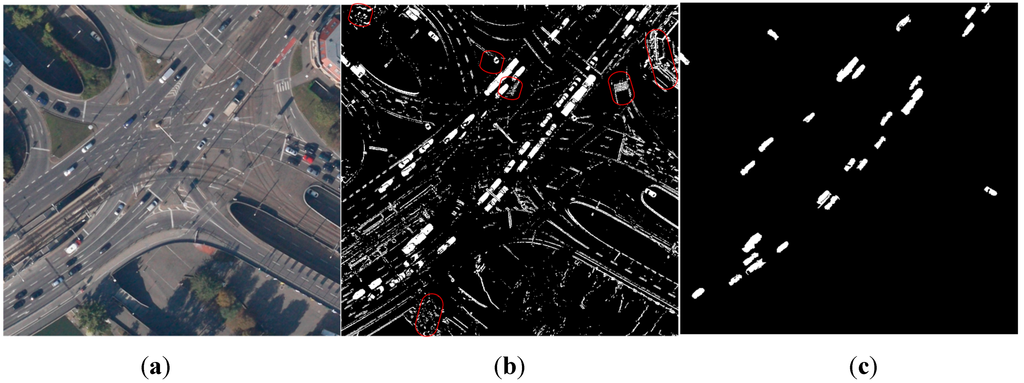
With the wide development of UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) technology, moving target detection for aerial video has become a popular research topic in the computer field. Most of the existing methods are under the registration-detection framework and can only deal with simple background scenes.
Read MoreFast Aerial Video Stitching
Jing Li, Tao Yang*, Jingyi Yu, Zhaoyang Lu, Ping Lu, Xia Jia, Wenjie Chen.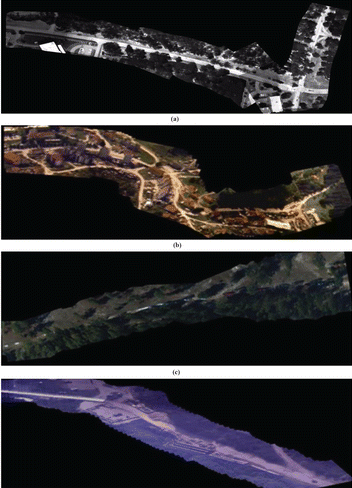
The highly efficient and robust stitching of aerial video captured by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is a challenging problem in the field of robot vision. Existing commercial image stitching systems have seen success with offline stitching tasks, but they cannot guarantee high-speed performance when dealing with online aerial video sequences.
Read MoreSimultaneous active camera array focus plane estimation and occluded moving object
TaoYang, YanningZhang, RuiYu, XiaoqiangZhang, TingChen, Lingyan Ran, Zhengxi Song,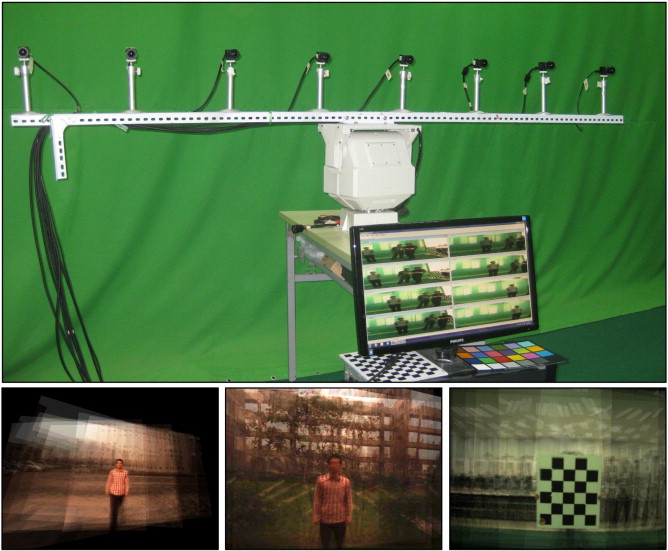
Automatically focusing and seeing occluded moving object in cluttered and complex scene is a significant challenging task for many computer vision applications. In this paper, we present a novel synthetic aperture imaging approach to solve this problem.
Read MoreA New Hybrid Synthetic Aperture Imaging Model for Tracking and Seeing People Through Occlusion
TaoYang, YanningZhang, Xiaomin Tong, XiaoqiangZhang, RuiYu,Robust detection and tracking of multiple people in cluttered and crowded scenes with severe occlusion is a significant challenge for many computer vision applications. In this paper, we present a novel hybrid synthetic aperture imaging model to solve this problem. The main characteristics of this approach are as follows.
Read MoreHigh Performance Imaging Through Occlusion via Energy Minimization-Based Optimal Camera Selection
TaoYang, Yanning Zhang, Xiaomin Tong, Wenguang Ma, Rui Yu,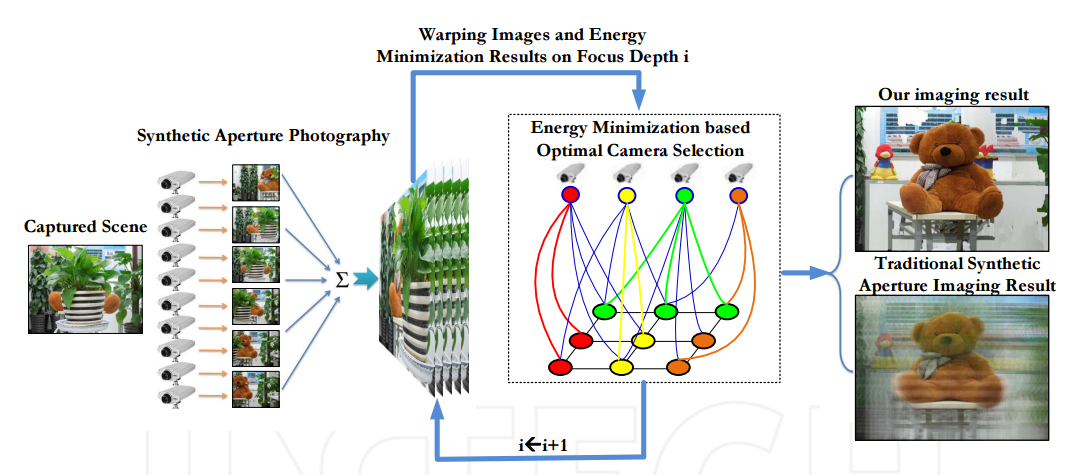
Seeing an object in a cluttered scene with severe occlusion is a significantly challenging task for many computer vision applications. Although camera array synthetic aperture imaging has proven to be an effective way for occluded object imaging, its imaging quality is often significantly decreased by the shadows of the foreground occluder.
Read MoreExploiting Loops in the Camera Array for Automatic Focusing Depth Estimation
TaoYang, Yanning Zhang, RuiYu, TingChen,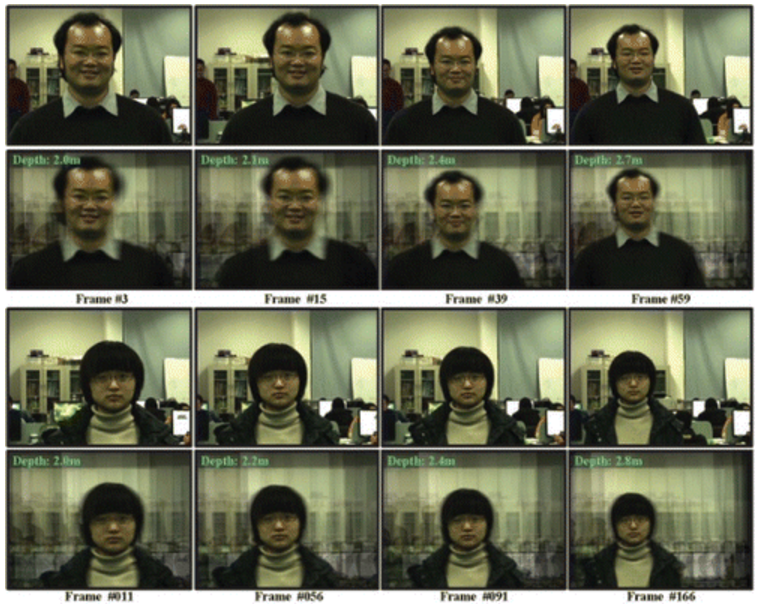
Abstract Autofocus is a fundamental and key problem for modern imaging sensor design. Although this problem has been well studied in single camera literature, unfortunately, little research has been done on large-scale camera arrays.
Read MoreA Novel Multi-Object Detection Method in Complex Scene Using Synthetic Aperture Imaging and vision computing
Zhao Pei, Yanning Zhang, Tao Yang, X. Zhang, and Y.H. Yang.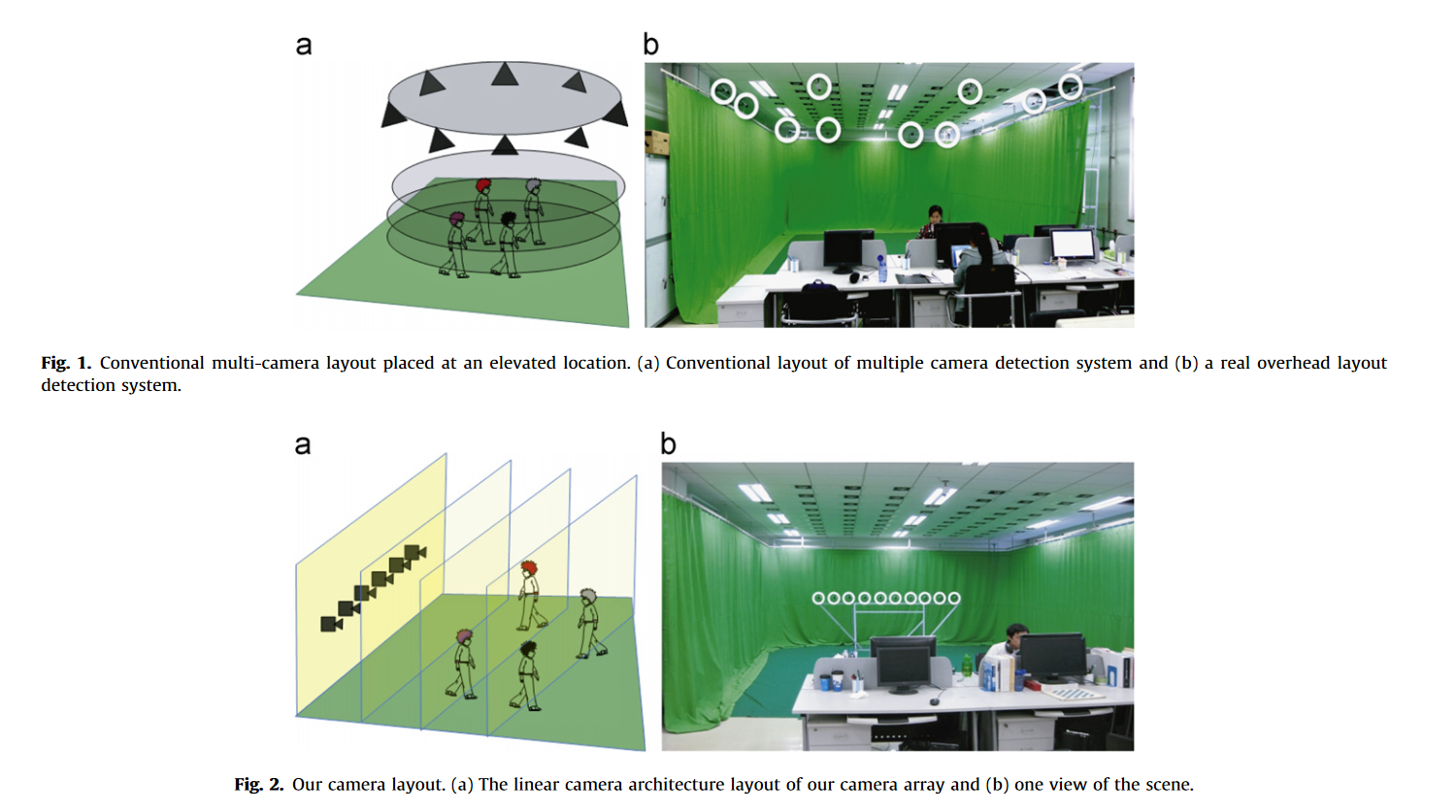
This paper proposes a novel multi-object detection method using multiple cameras. Unlike conventional multi-camera object detection methods, our method detects multiple objects using a linear camera array. The array can stream different views of the environment and can be easily reconfigured for a scene compared with the overhead surround configuration.
Read MoreClustering method for counting passenger getting in a bus with single camera
TaoYang, Yanning Zhang, DapeiShao, YingLi.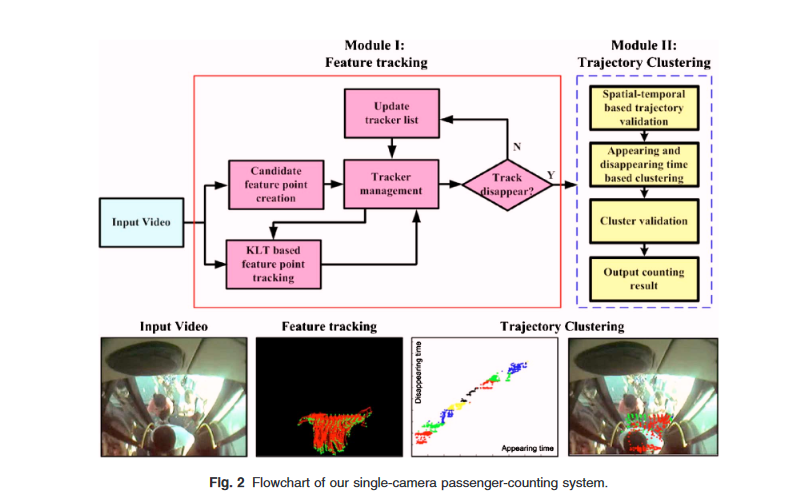
Automatic counting of passengers is very important for both business and security applications. We present a single-camera-based vision system that is able to count passengers in a highly crowded situation at the entrance of a traffic bus.
Read MoreRobust object tracking based on adaptive and incremental subspace learning
Xiaomin Tong,Yanning Zhang,TaoYang.The traditional target tracking algorithm usually trains the template with detected samples and updates the template at a fixed frequency. This close-loop mechanism lacks feedback and often makes it impossible to track targets robustly when target appearance or illumination changes.
Read MoreScene complexity and invariant feature based aerial video registration
TaoYang, Yanning Zhang, XiuweiZhang,Xingong Zhang.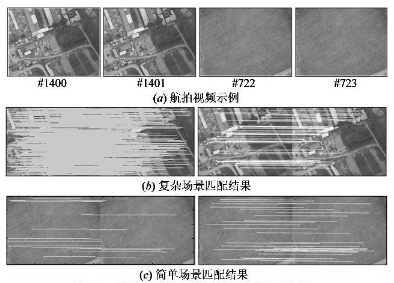
Real time and robust image registration is the premise and key technology of aerial video stabilization, panorama stitching and ground moving target detection and tracking. This paper presents a novel scene complexity and invariant feature based aerial video registration algorith.
Read MoreScene model and statistic learning based pedestrian detection
TaoYang,JingLi,QuanPan,Yanning Zhang.
A scene model and statistic learning based method for pedestrian detection in complicated real-world scenes is proposed. A unique characteristic of the algorithm is its ability to train a special cascade classifier dynamically for each individual scene.
Read MorePepole tracking through occlusion
TaoYang,JingLi,QuanPan,Yanning Zhang.This paper presents a novel real-time multiple object tracking algorithm, which contains three parts: region correlation based foreground segmentation, merging-splitting based data association and greedy searching based occluded object localization.
Read MoreCo-motion based CCD/IR video registration
Xiuwei Zhang,Yanning Zhang,TaoYang,Xingong Zhang,Dapei Shao.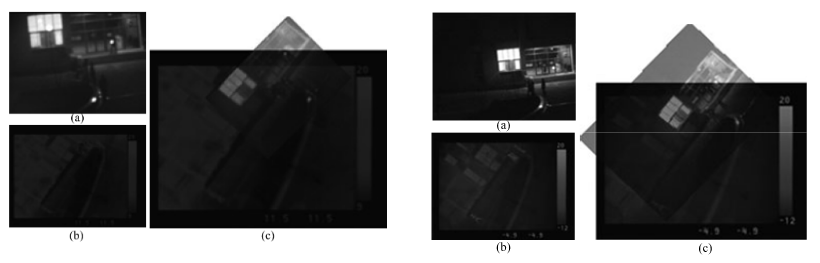
An automatic visual–thermal image sequence registration method based on co-motion was proposed. Different from other methods, co-motion (concurrent motions) statistics feature was adopted to regist heterogeneous image sequences.
Read MoreA multiple layer background model for foreground detection
TaoYang,JingLi,QuanPan,YongmeiCheng.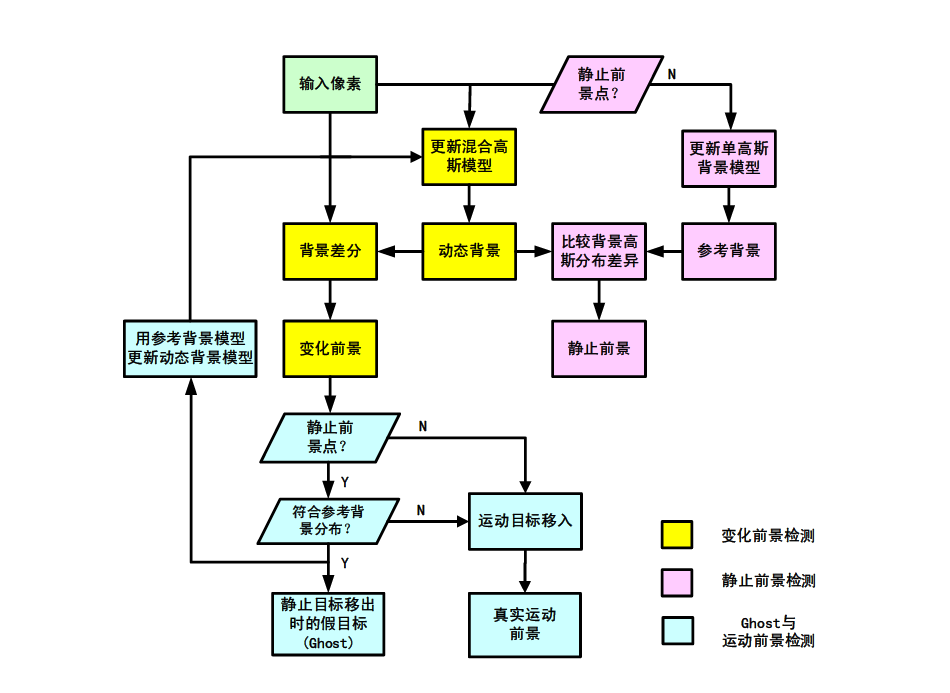
Foreground detection is an important research problem in visual surveillance. In this paper, we present a novel multiple layer background model to detect and classify foreground into three classes, moving object, static object and ghost. The background is divided into two layers, reference background and dynamic background.
Read More重要国际会议
Multiple Pedestrian Tracking Based on Multi-layer Graph with Tracklet Segmentation and Merging
Wencheng Duan, Tao Yang, Jing Li, Yanning Zhang.Multiple pedestrian tracking is regarded as a challenging work due to difficulties of occlusion, abrupt motion and changes in appearance. In this paper, we propose a multi-layer graph based data association framework to address occlusion problem. Our framework is hierarchical with three association layers and each layer has its corresponding association method.
Read MoreBands Sensitive Convolutional Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Lingyan Ran, Yanning Zhang, Wei Wei, Tao Yang.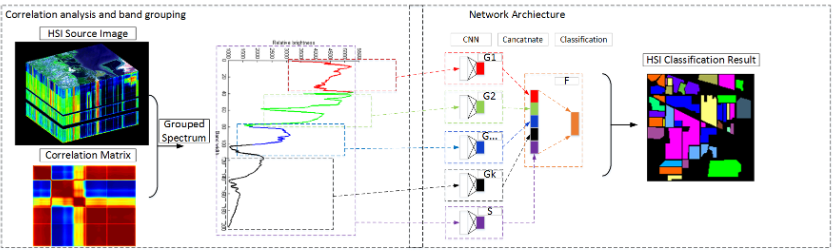
Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification deals with the problem of pixel-wise spectrum labelling. Traditional HSI classification algorithms focus on two major stages: feature extraction and classifier design. Though studied for decades, HSI classification hasn't been perfectly solved. One of the main reasons relies on the fact that features extracted by embedding methods can hardly match an ad hoc classifier.
Read MoreCompressive Tracking based on Superpixel Segmentation
Ting Chen, Hichem Sahli, Yanning Zhang, Tao Yang, Lingyan Ran.The compressive sensing trackers, which utilize a very sparse measurement matrix to capture the targets' appearance model, perform well when the tracked targets are well defined. However, such trackers often run into drifting problems due to the fact that the tracking result is a bounding box which also includes background information, especially in the case of occlusion and low contrast situations.
Read MoreAll-In-Focus Synthetic Aperture Imaging
Tao Yang, Yanning Zhang, Jingyi Yu, Jing Li, Wenguang Ma, Xiaomin Tong, Rui Yu, Lingyan Ran.
Heavy occlusions in cluttered scenes impose significant challenges to many computer vision applications. Recent light field imaging systems provide new see-through capabilities through synthetic aperture imaging (SAI) to overcome the occlusion problem.
Read More
Autonomous Near Ground Quadrone Navigation with Uncalibrated Spherical Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Lingyan Ran, Yanning Zhang, Tao Yang, Ting Chen.
This paper focuses on the use of spherical cameras for autonomous quadrone navigation tasks. Previous works of literature for navigation mainly lie in two categories: scene-oriented simultaneous localization and mapping and robot-oriented heading fields lane detection and trajectory tracking. Those methods face the challenges of either high computation cost or heavy labelling and calibration requirements.
Read MoreContinuously tracking and see-through occlusion based on a new hybrid synthetic aperture imaging model
TaoYang, YanningZhang, Xiaomin Tong, XiaoqiangZhang, RuiYu.Robust detection and tracking of multiple people in cluttered and crowded scenes with severe occlusion is a significant challenging task for many computer vision applications. In this paper, we present a novel hybrid synthetic aperture imaging model to solve this problem.
Read More
Real-time multiple object tracking with occlusion handling in dynamic scenes
TaoYang, Stan Z.Li ,Quan Pan, Jing Li.This work presents a real-time system for multiple object tracking in dynamic scenes. A unique characteristic of the system is its ability to cope with long-duration and complete occlusion without a prior knowledge about the shape or motion of objects. The system produces good segment and tracking results at a frame rate of 15-20 fps for image size of 320x240...
Read More
Robust people detection and tracking in a multi-camera indoor visual surveillance system
TaoYang, Francine Chen, Don Kimber, Jim Vaughan.In this paper we describe the analysis component of an indoor, real-time, multi-camera surveillance system. The analysis includes: (1) a novel feature-level foreground segmentation method which achieves efficient and reliable segmentation results even under complex condition...
Read More
DOTS: Support for effective video surveillance
Andreas Girgensohn, Don Kimber, Jim Vaughan, Tao Yang, Frank Shipman, Thea Turner, Eleanor Rieffel, Lynn Wilcox, Francine Chen, Tony Dunnigan.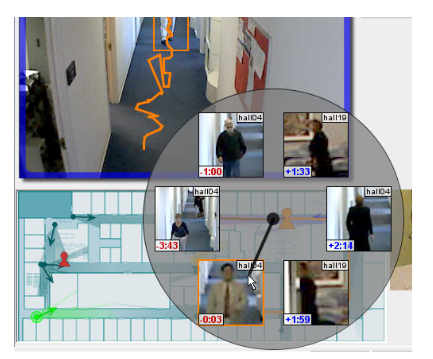
DOTS (Dynamic Object Tracking System) is an indoor, real-time, multi-camera surveillance system, deployed in a real office setting. DOTS combines video analysis and user interface components to enable security personnel to effectively monitor views of interest and to perform tasks such as tracking a person.
Read More
FlyingSword: A Real-time Motion Video Registration, Stabilization, Mosaicing and Moving Object Tracking System
TaoYang, Yanning Zhang.
Developing a fully automatic, efficient and robust video content analysis system is a subject of great scientific and commercial interest. Intelligent video content analysis with a static camera has been well researched over the past decade, and many excellent algorithms and systems have been proposed in the literature.
Read More
A Novel Multi-Planar Homography Constraint Algorithm for Robust Multi-People Location with Severe Occlusion
Xiaomin Tong, TaoYang, Runping Xi, Dapei Shao, Xiuwei Zhang.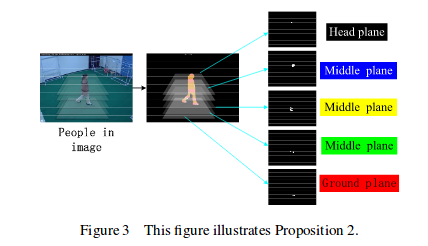
Multi-view approach has been proposed to solve occlusion and lack of visibility in crowded scenes. However, the problem is that too much redundancy information might bring about false alarm. Although researchers have done many efforts on how to use the multi-view information to track people accurately, it is particularly hard to wipe off the false alarm.
Read More
Active learning based pedestrian detection in real scenes
TaoYang, Jing Li, Quan Pan, Chunhui Zhao, Yiqiang Zhu. 18th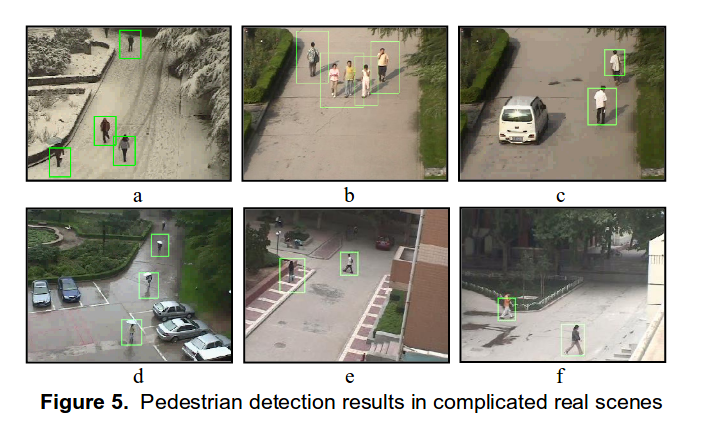
This work presents an active learning based method for pedestrian detection in complicated real-world scenes. Through analyzing the distribution of all positive and negative samples under every possible feature, a highly efficient weak classifier selection method is presented. Moreover, a novel boosting architecture is given to get satisfied False Positive Rate (FPR) and False Negative Rate (FNR) with few weak classifiers.
Read More
